Do House Wrens on Grenada have different songs in different places? In 2017 Marie-Ève Cyr, a masters student from the University of Manitoba, visited Grenada to find out. Read all about her research and the celebration of Grenada’s birds that Marie-Ève and her lab-mates held whilst on the Island.
Back in 2017, I had the chance to visit the island of Grenada and the southern West Indies on a field course with other students from the University of Manitoba. As a group, we were there to learn about the natural history of the island, local socioeconomics, and sustainable tourism. As a researcher with the Koper lab at the University of Manitoba, I also planned to study resident House Wrens. During our stay we were helped and guided by a multitude of wonderful local organizations, including Belmont Estate, SPECTO, and Almost Paradise Cottages.
Learning from each other
Beyond academic goals, we wanted to give back to the community. As part of the field course, we created the 2017 edition of Celebration of Grenada’s Birds Festival, hosted by Belmont Estate, where we taught local children about Grenada’s avian fauna. The festival was a success and an amazing experience. But during the field course, I also collected recordings of Grenada House Wren songs, and in October 2020, my colleagues and I published a paper about these recordings in the journal Bioacoustics. So, during our stay in Grenada, we learned from the community and they learned from us.
Click on photos below to view larger and see captions.
Changing their tune in the city
This research on Grenada House Wrens started from discussions with other Canadian students who had visited Grenada before me. We were discussing how the Grenada House Wrens appeared to sing differently from those they usually hear in Canada; and that there were variations in their song across the island. However, we could not find any studies on House Wren songs in Grenada. My interest was piqued! Because my background is the study of the effect of noise and human activity on birds, those two ideas merged in my mind. I focused my attention on figuring out whether those differences in the House Wren songs that my colleagues had identified were associated with the human presence in their environment. As it turned out, my colleagues were right. House Wrens did sing differently in different parts of the island, and adjusted their song when living in urban habitats.
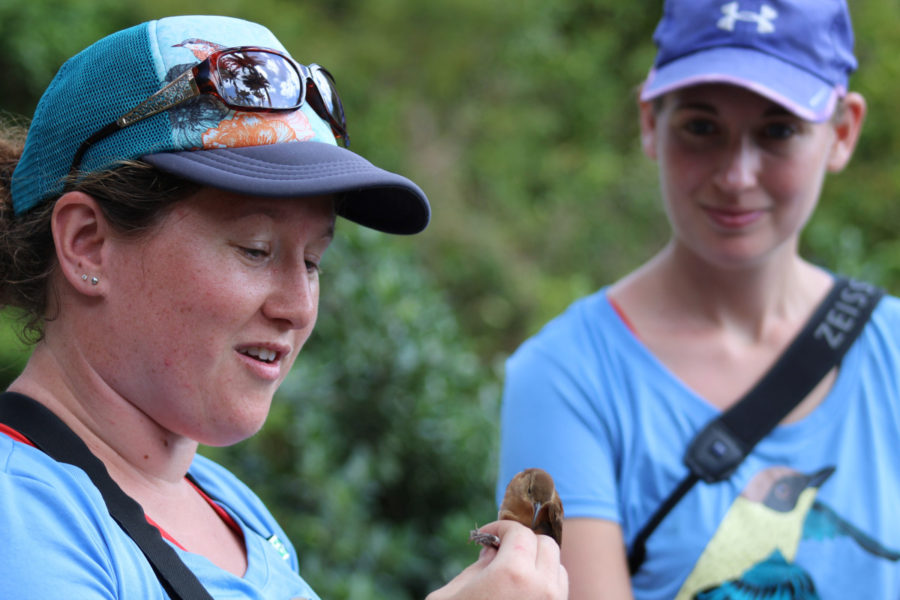

Singing in different spaces
House Wrens are found throughout North and South America. They are one of the most widely distributed species and their song is extremely variable. With a variety of life history traits throughout its range, there is some discussion about the status of the House Wren as a single species with over 30 recognized subspecies. Could one or more of these subspecies qualify as full species?
Accompanied by two colleagues, I recorded House Wrens in five urban areas and five rural areas in Grenada in 2016 and 2017. Grenada is a Small Island Developing State, where cities are characterized by buildings a few storeys tall. The capital of St. George’s has fewer than 40,000 inhabitants. This contrasts greatly with big cities in North America and makes this research all the more interesting. Since most of the literature regarding urbanization and its impact on birds was done in North American cities, it is hard to look at them within the context of Grenada. We felt that birds in Grenada, including House Wrens, might deal with the challenges of urban environments differently.
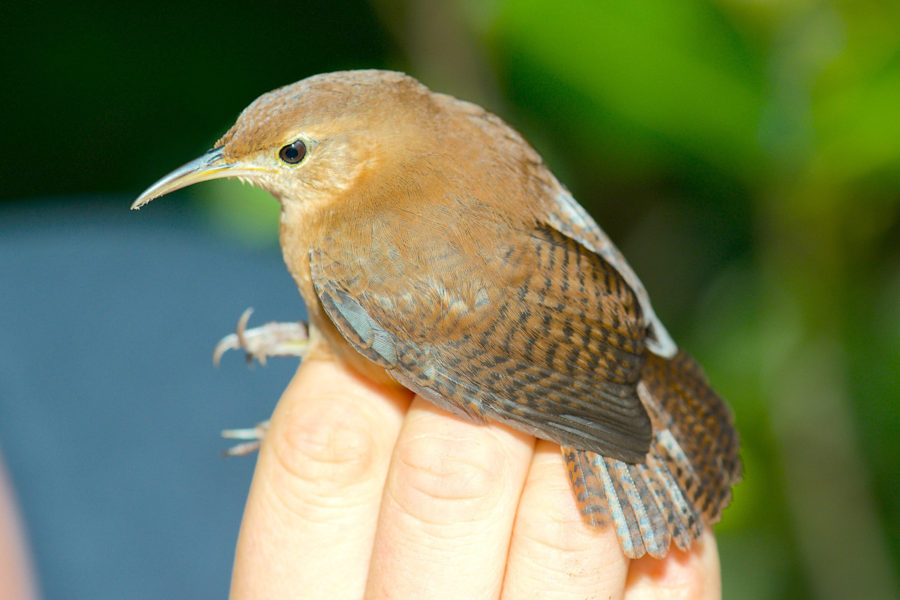

Competing with the humans
We found that House Wrens did adjust their singing style in urban areas to improve their communication, using a mix of strategies. As is often observed in North American birds, they increased the lower frequency of part of their songs, specifically the introductory part. This reduces the masking of their song caused by the noise created by humans. However, unlike their North American counterparts, they sang faster trills in urban habitats. Fast trills can quickly disappear in closed habitats, but can also transmit further. This might explain why Grenadian House Wrens increase the number of trills as a compensatory mechanism in urban settings. It also suggests that birds in Grenada, and in other parts of the Caribbean, face different challenges compared to birds in larger North American cities. Why might this be?
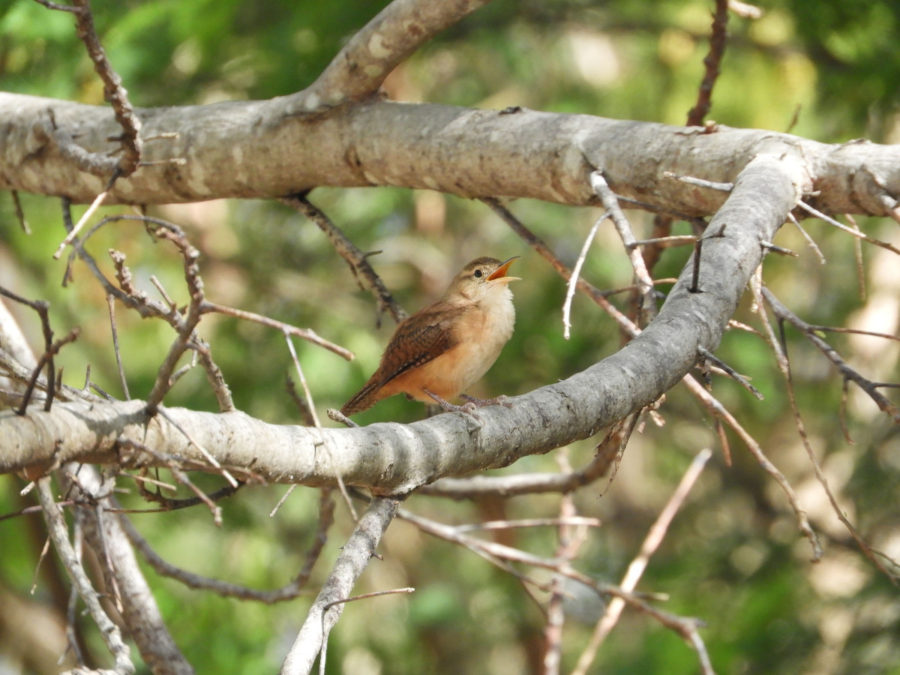

Birds and buildings
The high number of large and tall buildings, such as skyscrapers, in North American cities create a closed environment. There are lots of opportunities for echoes and the reverberation of sounds from the walls of buildings. But in Grenada, the dense and tall surrounding forest might actually be more closed than urban surroundings. Buildings in Grenada’s towns are generally less than four storeys tall, are not very close together, and are separated by roads. This is a good reminder that socio-economic context is important to consider, and bioacoustics research should expand its scope outside North America. More research from the Koper lab is ongoing in Grenada—there is much more to learn, so stay tuned!
Want to learn more?
Check out our publication in Bioacoustics: Marie-Ève Cyr, Kimberley Wetten, Miyako H. Warrington and Nicola Koper. 2020. Variation in song structure of House Wrens living in urban and rural areas in a Caribbean Small Island Developing State. Bioacoustics
Marie-Ève Cyr is a graduate student working on her Master of Natural Resource Management in the lab of Professor Nicola Koper at the University of Manitoba. Her current focus is on bioacoustics research and conservation biology, studying bird species under anthropogenic pressures in the Canadian prairies and the Caribbean.
Dr. Nicola Koper is a Professor in the Natural Resources Institute of the University of Manitoba. She studies avian conservation biology in Canada and the Neotropics. Currently, she is focusing on effects of anthropogenic noise, oil and gas activity, and agroecology of birds.
Click on photos below to view larger and see captions.








