This festive season we introduced 12 fascinating Caribbean birds in our twist on the classic carol The Twelve Days of Christmas. This English Christmas carol was first published in 1780, and presented without accompanying music, in a children’s book of poems and stories Mirth Without Mischief.
This festive season we introduced 12 fascinating Caribbean birds in our twist on the classic carol The Twelve Days of Christmas. This English Christmas carol was first published in 1780, and presented without accompanying music, in a children’s book of poems and stories Mirth Without Mischief.
It is believed that The Twelve Days of Christmas was intended to help young Catholics learn the tenets of their faith. However, this theory has been widely contested. The origins of the carol are unknown but perhaps it was written as a memory game.
We are certain, however, that no other Christmas carol features birds quite as prominently as The Twelve Days of Christmas. The lyrics are from old Europe with birds that are not found in the Caribbean. We thought it was time for an upbeat version so we put the spotlight on some magnificent migratory and endemic birds of the Caribbean!
If you follow us on social media (Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn), we shared a new bird every day or two for the last several weeks. (#12CaribBirdsOfChristmas) Here, we compile all the bird profiles into one blog in case you are not on social media, missed any, or would like to learn more about these amazing birds.
We really enjoyed curating posts for this series and had the pleasure of reading your lovely comments. Thank you for following along, bird after bird, with us. Let us know which bird was your favorite and why in the comments below .
And do sing along with us on our remix of this classic song! Any singers/ musicians out there—we would love to hear your recorded rendition of the song!!!
Photo credits: West Indian Whistling Duck by Ray Robles, Fernandina’s Flicker by Ken Pinnow, White-breasted Thrasher by Hank Tseng and Adams Toussaint, St Vincent Parrot by Nandani Bridglal , Golden Swallow by Francisco Alba, Jamaican Blackbird by Tom Johnson (ML890623210), Guadeloupe Woodpecker by Frantz Delcroix, Grenada Dove by Greg Homel, Bahama Oriole by Dan Stonko
Twelve Birds of Christmas – BirdsCaribbean Remix
An Oriole in a Pine Tree – Bahama Oriole
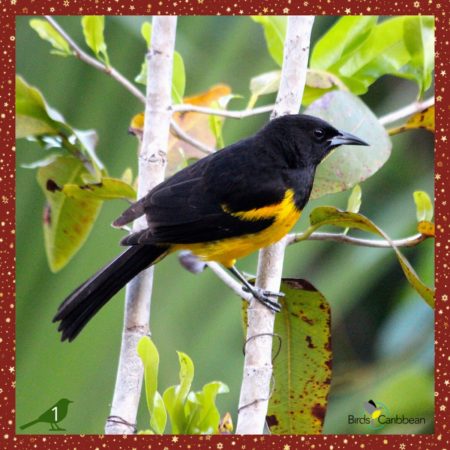 🎄On the first day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, A Partridge in a Pear Tree.🎶 But wait, that doesn’t seem quite right for the Caribbean 🤔, so let’s turn up the heat ☀️, amp up the vibrancy, migrate south 🌎, and what do we get…. An oriole in a pine tree 🌲 . That is, of course, the Bahama Oriole. This striking bird stands bright at the tree tops boasting shiny black ⚫️ plumage on its head, back and chest, and bright yellow 🟡 plumage on its shoulders, belly, and rump. It can only be found on Andros Island in the Bahamas 🇧🇸 , where it nests in native pine forests.
🎄On the first day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, A Partridge in a Pear Tree.🎶 But wait, that doesn’t seem quite right for the Caribbean 🤔, so let’s turn up the heat ☀️, amp up the vibrancy, migrate south 🌎, and what do we get…. An oriole in a pine tree 🌲 . That is, of course, the Bahama Oriole. This striking bird stands bright at the tree tops boasting shiny black ⚫️ plumage on its head, back and chest, and bright yellow 🟡 plumage on its shoulders, belly, and rump. It can only be found on Andros Island in the Bahamas 🇧🇸 , where it nests in native pine forests.
Unfortunately, this bird faces multiple threats, including brood parasitism from the Shiny Cowbird, depredation by free-ranging domestic cats 🐈 , and habitat loss due to logging and residential development 🏘. There’s also the looming threat of increasingly frequent and severe hurricanes that could easily wipe out the Bahama Oriole’s entire small population 📉.
However, all hope is not lost! ✨ Our partners at the Bahamas National Trust and University of Maryland, Baltimore Maryland are doing exciting research to learn more about this species 🤓 and educating local communities on Andros about the importance of its pine forests. Click here for more facts ℹ️, to listen to its song 🎵, and free Bahama Oriole themed activities 🧩 for adults and children!
Two Grenada Doves
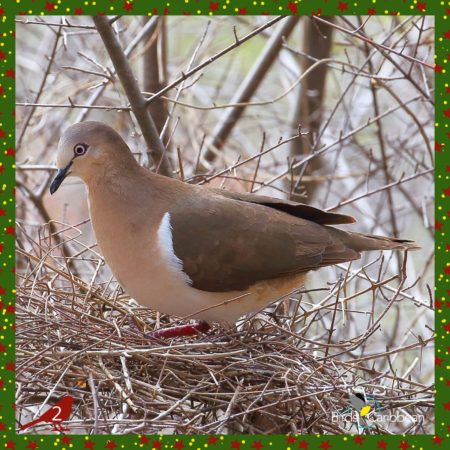 🎄The second day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Two Turtle Doves 🎶. Those turtle doves are adorable ☺️, but come on down to the southern Caribbean 🌎 and we can do you one better – two Grenada Doves!
🎄The second day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Two Turtle Doves 🎶. Those turtle doves are adorable ☺️, but come on down to the southern Caribbean 🌎 and we can do you one better – two Grenada Doves!
As their name implies, these shy and elusive birds live only on the island of Grenada 🇬🇩. This somewhat plump dove has brown 🟤 upperparts, buffy cinnamon-colored chest and neck, and grayish forehead, face and crown, with bright pinkish-red 🔴 statement legs and feet. How can you tell you’re looking at the ultra-rare Grenada Dove and not another dove 🧐? Be sure to take a look at its belly where you’ll find a strip of white ⚪️ feathers that extends from its side up around the bend of the wing!
The Grenada Dove prefers the coastal dry forests of deciduous thorn-scrub thickets and some emergent trees 🌳. Watch your step 👣 as these doves are typically found on the ground, searching for food; small seeds, fruits 🫐 and insects 🪱. IBut if you aren’t lucky enough to see this dove, keep an ear 👂 out for its characteristic call 🎶 which is a single descending note hooooooo that is repeated every 7-8 seconds.
Two Protected Areas have been established for the conservation of the Grenada Dove, but habitat loss remains a major threat. Its coastal habitats are unfortunately prime areas for development by the tourism 🏝 and industry sectors 🏭. We have been working with our partners in Grenada to try and halt 🛑 these unsustainable developments as well as remove mongoose, invasive predators of the Grenada Dove. Click here to learn more about the Grenada Dove, listen to its song, and access free activities.
With your support 🙌🏽, we can continue to protect the Critically Endangered Grenada Dove as we work to reverse the trend of habitat loss for this beautiful species. ✨Please consider making a donation.
Three French Peckers – Guadeloupe Woodpecker
 🎄On the third day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Three French hens 🎶. To be honest, that’s not a bad gift 🎁 at all, especially if those hens are good layers 🥚. But domestic fowl 🐓 pale in comparison to some of the wild French birds you can find in the Caribbean 😎, including the Trois Toto bwa —un oiseau magnifique found only in Guadeloupe 🇬🇵! In local French Creole the Guadeloupe Woodpecker is called Toto bwa for the tapping noise it makes.
🎄On the third day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Three French hens 🎶. To be honest, that’s not a bad gift 🎁 at all, especially if those hens are good layers 🥚. But domestic fowl 🐓 pale in comparison to some of the wild French birds you can find in the Caribbean 😎, including the Trois Toto bwa —un oiseau magnifique found only in Guadeloupe 🇬🇵! In local French Creole the Guadeloupe Woodpecker is called Toto bwa for the tapping noise it makes.
It appears to be an all black bird ⚫️ however its head and upperparts actually have a blue glossy sheen. Their underparts are a sooty black except for a reddish 🔴 hue on the chest and their tail feathers are brownish-black with blue-black legs. Females look like the male, but are smaller 📏. Interestingly, there are size differences within the island—woodpeckers found on the peaks of Basse-Terre are slightly bigger than those of Grande-Terre!
These fine French birds inhabit all different forest types, including swamp forests and mangroves, but they rely on dead coconut palm trees 🌴 for nesting. They are monogamous and pairs remain in their territory throughout the year. Young woodpeckers will take about a month 📆 to fledge and afterwards juveniles spend several months with their parents. They might even hang around until the next breeding season.
Although considered a Least Concern species, this handsome woodpecker is restricted to the island of Guadeloupe and is threatened by hurricanes 🌀, habitat conversion 🏘 and the removal of dead trees which they depend upon for nesting. Continued protection of this species and conservation of its habitats will help ensure that this beautiful species survives for future generations to enjoy! ✨
For more fun facts about this endemic woodpecker click here!
Four Blackbirds – Jamaican Blackbird
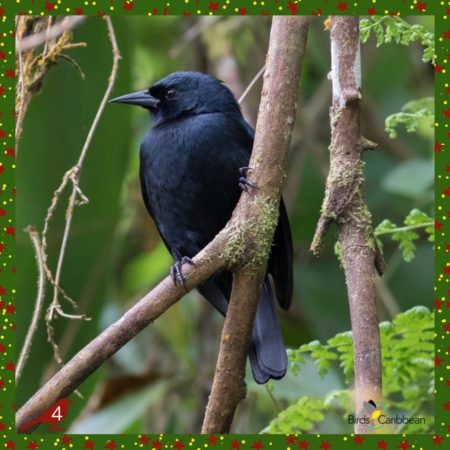 🎄The fourth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Four colly birds 🎶. But you had no idea what those were 💬. Did you say “colly birds” or “calling birds”? Our basic research 💻 suggests both phrases are correct, though “colly” is the Old English word for coal while “calling” refers to birds that “call out” in song, or songbirds. Either way, it’s an odd gift, so today we’re featuring a Jamaican endemic that fits both versions; the Jamaican Blackbird 🇯🇲.
🎄The fourth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Four colly birds 🎶. But you had no idea what those were 💬. Did you say “colly birds” or “calling birds”? Our basic research 💻 suggests both phrases are correct, though “colly” is the Old English word for coal while “calling” refers to birds that “call out” in song, or songbirds. Either way, it’s an odd gift, so today we’re featuring a Jamaican endemic that fits both versions; the Jamaican Blackbird 🇯🇲.
High up in Cockpit Country and the Blue and John Crow Mountains ⛰ National Park lives the Jamaican Blackbird. It is Endangered, with the greatest threat to its populations stemming from Bauxite mining, agriculture 🌾 and human developments 🏘. This taxonomically and ecologically distinct bird is all black with a slight blue gloss, short bill, legs and tails. Unlike other blackbirds it is mostly found feeding high in the trees 🌳 in montane forest. It feeds by pecking, like a woodpecker, in bromeliads, lichens and mosses, but will also probe tree bark and cavities for beetles 🪲 and caterpillars 🐛 . This bird is more likely to be heard than seen. Its song is a wheezy whee-whee-oooo; common call is a squeaky wheet. 🎶
Learn more about this fascinating bird here. This species was also an inspiration for an amazing bird song album by our partner Shika Shika, undertaken to raise funds to protect endangered birds in Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean – check out the project and songs here.
✨Together with our on-the-ground partners we work to protect incredibly unique birds like the Jamaican Blackbird that are threatened by habitat loss. Please consider making a contribution and give the gift 🎁 of birds to future generations.
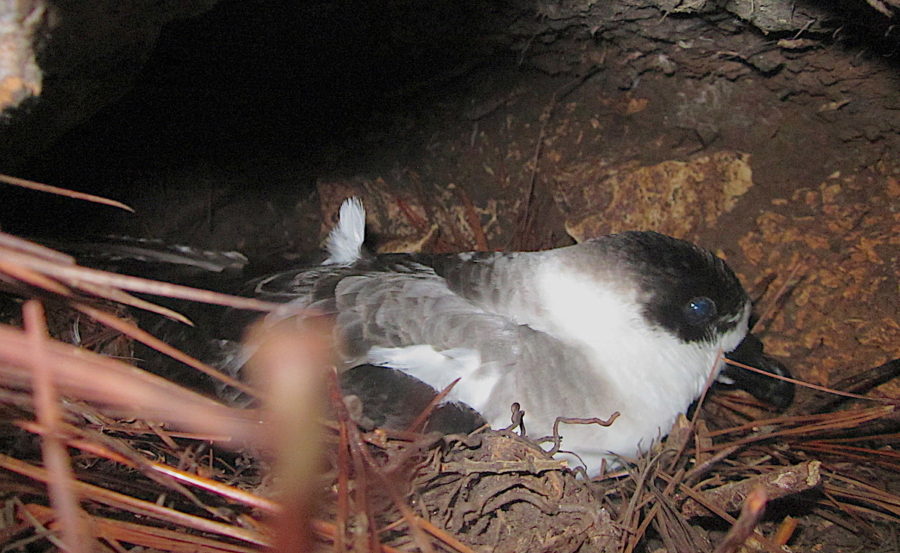
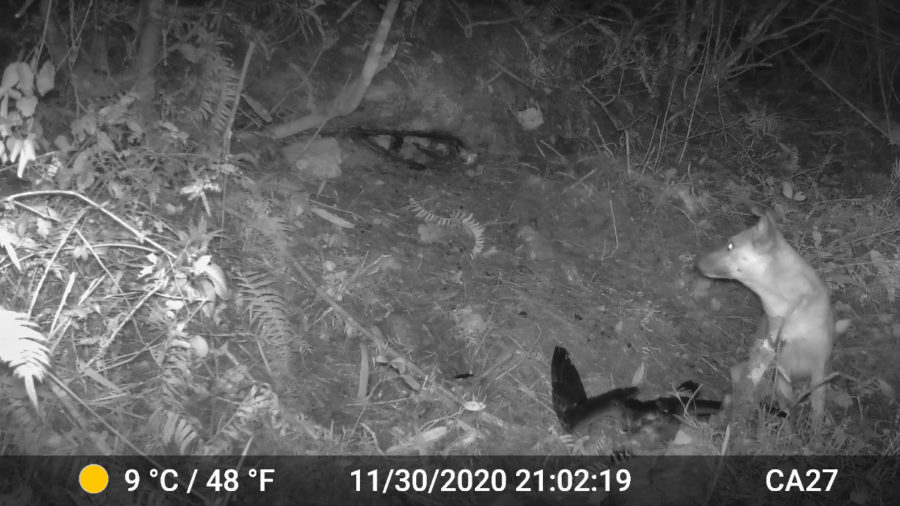
Five Golden Swallows
 🎄The fifth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me…Five gold rings 🎶. But you’re not a materialistic person, nor can you tolerate the environmental impact that comes with the extraction of precious metals 💍, so you looked your lover 💞 in the eye and said “Honey, I’d rather see gold in its natural form – take me birding for Golden Swallows!”
🎄The fifth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me…Five gold rings 🎶. But you’re not a materialistic person, nor can you tolerate the environmental impact that comes with the extraction of precious metals 💍, so you looked your lover 💞 in the eye and said “Honey, I’d rather see gold in its natural form – take me birding for Golden Swallows!”
The upperparts of male Golden Swallows often appear golden ✨ but are ever-changing as they fly around and catch the sunlight ☀️ at different angles. In a few seconds you might observe a blue-ish 🔵 sheen changing to a golden iridescence that then changes to an olive-green 🟢! Their underparts are white with dusky bronze-green wings and tail. The female on the other hand, is duller, with some gray-brown mottling on the chest.
One can spend hours ⏳ watching and being entertained by these amazing birds as they twist 🔀, turn ⤴️ , and dive ⤵️ through the air with incredible grace and precision. They feed on airborne insects like beetles 🪲 and wasps.
The Golden Swallow has disappeared from the island of Jamaica 🇯🇲 and is restricted to patches of montane pine forest🌲in Hispaniola. They have possibly disappeared from Jamaica due to lack of food. Insect populations have been steadily decreasing 📉 due to destruction of native habitats as well as the widespread use of chemicals to kill insects ☠️. The good news is that everyone can help by planting native plants 🌱 at home. Native plants attract native insects, and these insects provide lots of food for MANY different bird species 😃.
Learn more about the Golden Swallow and access free activities and resources here. Read about our VP 👨🏻💼 Justin Procter’s quest to find the Golden Swallow in Jamaica’s Ram Goat Cave.
Six Songbirds Singing – Summer Tanager
 🎄The sixth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Six Geese-a-laying🎶. While we often think of egg-laying as a beautiful, miraculous event (and it is), have you given any thought to the size of those eggs and the mechanics involved🤔? Needless to say, six geese-a-laying won’t be a peaceful scene, but rather a headache of hissing and honking 📣. Let’s reduce holiday stress where we can and consider down-sizing to six songbirds singing 🎶 instead.
🎄The sixth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Six Geese-a-laying🎶. While we often think of egg-laying as a beautiful, miraculous event (and it is), have you given any thought to the size of those eggs and the mechanics involved🤔? Needless to say, six geese-a-laying won’t be a peaceful scene, but rather a headache of hissing and honking 📣. Let’s reduce holiday stress where we can and consider down-sizing to six songbirds singing 🎶 instead.
‘Songbirds’ are beautiful passerine birds with melodious songs, a great example is the Summer Tanager. This neotropical migrant has strawberry 🍓 coloured plumage and is quite vocal. Its call is described as pi-tuck or pi-ti-tuck or ki-ti-tuck while its song is similar to that of an American Robin with a series of warbling phrases.
The Summer Tanager is one of many songbirds illegally captured 📦 in Cuba for the pet trade. Although it has a beautiful song, this bird is mainly captured for its ornamental beauty. Sadly, many migratory songbirds like the Indigo Bunting and Rose-breasted Grosbeak, and resident/ endemic birds like the Cuban Bullfinch and Cuban Grassquit, are targeted by trappers for their singing abilities.
Songbird competitions are very popular in Cuba 🇨🇺, Trinidad 🇹🇹, and Venezuela 🇻🇪 , with betting and cash prizes 💰 for the best singer. These birds are inhumanely trapped using cages with lures, perches covered with glue, and nets. Many die from the process or soon after due to improper care. The surviving birds are readily offered for sale on social media 📲 platforms reaching more potential buyers. The songbird trade is rampant in the Caribbean and is emptying our forests of both song and life 😞.
ℹ️ For more information about the alarming numbers of birds illegally captured in Cuba and our proposed strategies to combat this unsustainable and cruel trade please read our investigative report.
This crisis can end with your support 🙌🏽! Please consider making a contribution here. Your gift will help us in our appeals to local governments to enforce the laws mandated to protect birds, help our partners develop a national media campaign, and create other livelihoods like eco-tourism 🏞.
Seven Parrots Squawking – St. Vincent Parrot
 🎄The seventh day of Christmas, my true love sent to me Seven Swans a-Swimming🎶. Swans 🦢 are the universal symbol of grace and beauty🪞. But here in the Caribbean, Christmas is a time for noisy merriment and flocking together 🎊 so we present you with Seven Parrots Squawking!
🎄The seventh day of Christmas, my true love sent to me Seven Swans a-Swimming🎶. Swans 🦢 are the universal symbol of grace and beauty🪞. But here in the Caribbean, Christmas is a time for noisy merriment and flocking together 🎊 so we present you with Seven Parrots Squawking!
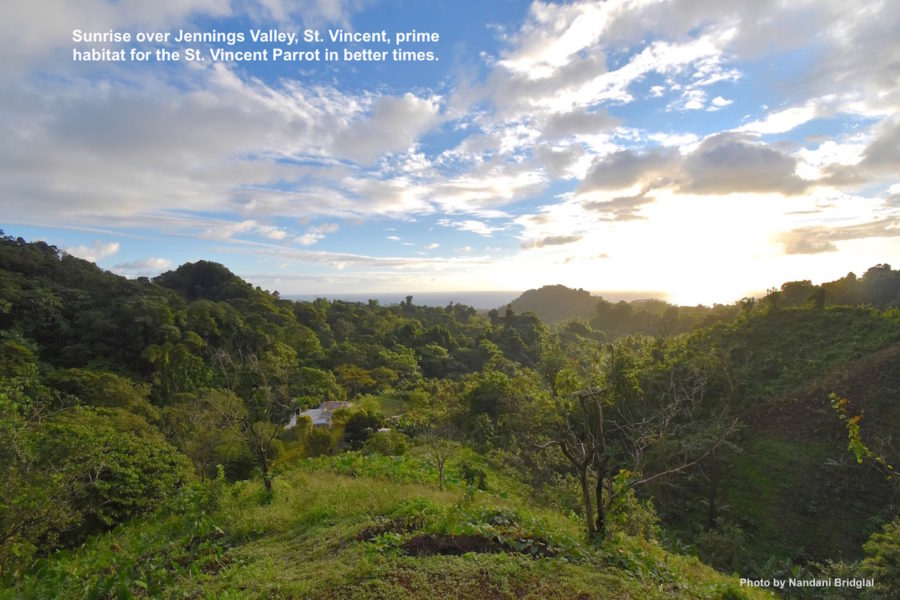
The striking Saint Vincent Parrot 🦜 is the national bird of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 🇻🇨 and is endemic to the island. If you look carefully, it has the yellow 🟡, blue 🔵 and green 🟢 colours of the national flag, making it extra special to Vincentians!
There are two colour morphs for this uniquely coloured parrot: yellow-brown (more common) and green. Both have pale heads and bronze-colored underparts, a blue, yellow and orange tail, and green-and-blue flight feathers.
The Saint Vincent Parrot can be found in mature rainforest 🏞 along western and eastern slopes of the island’s central mountain range and, occasionally, in nearby cultivated lands. They are loud birds with an impressive vocal repertoire, so listen for their call 🎶 in the early morning ☀️ or late afternoon when they are most active! Males and females look similar and are usually seen flying in pairs but have been observed in flocks foraging on fruits 🥭, seeds, flowers 🌺 and leaves.
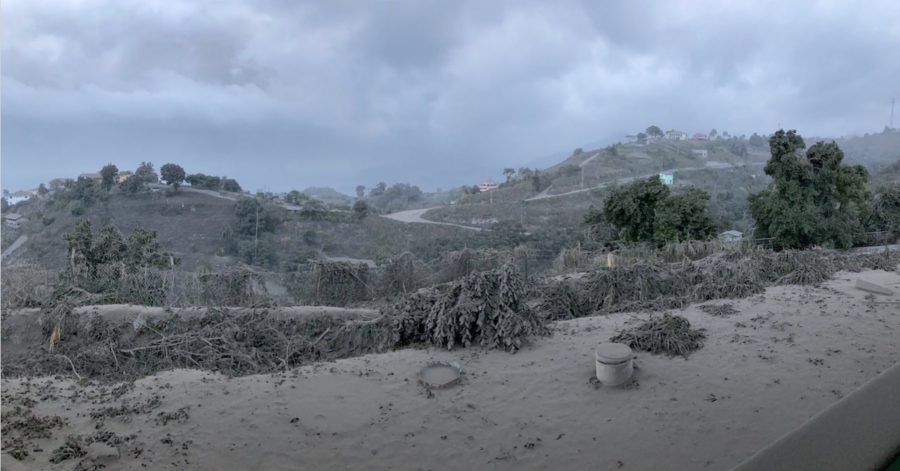
Its small population of around 850 birds has been slowly increasing however, this vulnerable parrot suffered devastating habitat loss and food scarcity after the La Soufriere volcanic eruptions 🌋 earlier this year. With assistance from BirdsCaribbean donors and other partners, the St Vincent Forestry Dept has been working hard to assess the status of the parrot and restore habitat. You can help to save this iconic bird from extinction. ✨.
Click here for more facts, to listen to its call, and free Saint Vincent Parrot themed activities 🧩 for adults and children!
Eight Thrashers Thrashing – White-breasted Thrasher
 🎄The eighth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Eight Maids-a-Milking🎶. In 15th and 16th century England, the phrase “let’s go-a-milking” was a euphemism for “let’s get married.” 💍 We’re going to update this to the 21st century with a spunky yet elegant Caribbean bird and give you Eight Thrashers Thrashing! While you may not want these birds in your house at Christmas time, they certainly are dashing 🎩!
🎄The eighth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Eight Maids-a-Milking🎶. In 15th and 16th century England, the phrase “let’s go-a-milking” was a euphemism for “let’s get married.” 💍 We’re going to update this to the 21st century with a spunky yet elegant Caribbean bird and give you Eight Thrashers Thrashing! While you may not want these birds in your house at Christmas time, they certainly are dashing 🎩!
The White-breasted Thrasher, with a chocolate brown 🟤 back, striking white chest, and piercing red 🔴 eye, was described by James Bond as “one of the rarest birds in the West Indies.” Not surprisingly, Bond was onto something! Found only in Saint Lucia 🇱🇨 and Martinique 🇲🇶, where it is known as Gòj Blan and Moqueur Gorge Blanche, respectively, there are fewer than 2,000 thrashers left. White-breasted Thrashers also display a unique behavior called cooperative breeding, where they delay independent breeding, and instead help their parents in raising their siblings – how lucky for Mom and Dad 😊!
The White-breasted Thrasher population is thought to be declining 📉 due to increased predation by non-native invasive species, such as rats 🐀 , domestic cats 🐈 , and mongoose. Our incredible partners in Saint Lucia safely continued their critical work throughout the pandemic and recorded a total of 19 White-breasted Thrasher nests in 2020 🏆
✨Learn more about this unique and endangered species here.
For more information on the White-breasted Thrasher Species Recovery Plan and field work by our partners 📑, supported in part by BirdsCaribbean donors , click here.
Nine Flickers Flicking – Fernandina’s Flicker
 🎄On the 9th day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, nine drummers drumming🎶. But of course no drum sticks or snare drums 🥁 showed up, because your true love has style 😎, and appreciates nature’s real drummers – the woodpeckers! So pop some aspirin 💊 and get ready for the ensuing explosive sound of nine Fernandina’s Flickers tearing apart your house’s 🏠 new cedar wood siding.
🎄On the 9th day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, nine drummers drumming🎶. But of course no drum sticks or snare drums 🥁 showed up, because your true love has style 😎, and appreciates nature’s real drummers – the woodpeckers! So pop some aspirin 💊 and get ready for the ensuing explosive sound of nine Fernandina’s Flickers tearing apart your house’s 🏠 new cedar wood siding.
The island of Cuba 🇨🇺 is home to one of the world’s most threatened flickers – the Fernandina’s Flicker. The male has a buff-cinnamon head with fine black ⚫️ streaking. It has a distinct black malar stripe, sometimes with a red tinge. This mark is absent ❌ in the female. Chin and throat are heavily but finely streaked black. Its bill is black, long, pointed and curved. Its body and tail are largely barred mustard yellow 🟡 and black.
Interestingly you’re likely to see this woodpecker foraging on the ground, in open woodlands and savanna-palm 🌴 habitats, for insects 🕷 , seeds, and worms 🪱 . Pairs nest in both live and old hollowed-out palms and share these breeding trees with other secondary cavity nesting birds such as the American Kestrel, and fellow-endemics the Bare-legged Owl 🦉 and Cuban Parakeet 🦜. During the breeding season, however, the West Indian Woodpecker and Fernandina’s Flicker fight for nesting sites 😠, even though the nesting holes were most likely excavated by the West Indian Woodpecker! The West Indian Woodpecker is very territorial, they will even destroy eggs 🥚 and remove chicks 🐣 of other secondary nesting birds, including those of the Fernandina’s Flicker!
Its population is estimated at no more than 400 pairs with the largest occurring in the Zapata Swamp. It was once common across Cuba but habitat loss due to logging and conversion for agriculture 🌱 have resulted in its patchy distribution. Another major driver is loss of prime nesting sites when dead palms are cut down to illegally collect parrots and parakeets for the pet trade 😞. Learn more about this Cuban endemic here.
Ten Plovers Piping – Piping Plover
 🎄On the tenth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Ten Pipers Piping🎶. But we’re still in a pandemic 😷 and, where you are, gatherings might be restricted 🚫. Instead we present you with 10 Plovers Piping 😀.
🎄On the tenth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, Ten Pipers Piping🎶. But we’re still in a pandemic 😷 and, where you are, gatherings might be restricted 🚫. Instead we present you with 10 Plovers Piping 😀.
Small, chubby, and adorable ☺️, the Piping Plover is a sand-coloured shorebird with white underparts, a black ⚫️ neck band, orange 🟠 legs, and a short stubby beak. Most striking of all, its dark round eyes that give it that “I’m a good cuddler” look. They have a two-part piping whistle 🎵 that drops in pitch, pwee-doo.”
The Piping Plover breeds in North America but heads south for the winter 🌎. They do not go as far south as other shorebirds, instead they stop off in The Bahamas 🇧🇸 , Turks and Caicos Islands 🇹🇨 and Cuba 🇨🇺 . You are most likely to find them on open sandy beaches, wetlands, and mudflats feeding on small invertebrates. It is also a pretty clever feeder. On the beach 🏝 , after a wave 🌊 rolls up and leaves a glassy film, the Piping Plover will extend one foot slightly forward and vibrate it against water-saturated sand bringing invertebrates in the sand to the surface before pecking 🍽.
Developments on beaches 🏙 and lake shores mean Piping Plovers have lost some of their breeding habitats and are now far less common than they used to be 😔. Nesting areas on beaches are now often protected ⚠️ from disturbance to try to help the population grow.
Making sure they have safe places to feed and rest 💤 in the Caribbean during the winter is also important. Click here for some tips on how you can #ShareTheShore with these lovable little shorebirds. And learn more about the Piping Plover and access free activities and resources here.
Eleven egrets dancing – Reddish Egret
 🎄The eleventh day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, eleven ladies dancing 💃🏻. Your true love 💗 may have been trying to pull a fast one, knowing all too well that the men usually dance to get the ladies’ attention in the animal kingdom! In the spirit of gender equality, you both get in on the dancing 💃🏻🕺🏻, showing off snazzy moves inspired by Eleven Egrets Dancing.
🎄The eleventh day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, eleven ladies dancing 💃🏻. Your true love 💗 may have been trying to pull a fast one, knowing all too well that the men usually dance to get the ladies’ attention in the animal kingdom! In the spirit of gender equality, you both get in on the dancing 💃🏻🕺🏻, showing off snazzy moves inspired by Eleven Egrets Dancing.
The Reddish Egret is a relatively large and elegant 🪞 bird known for its entertaining feeding behavior – often described as a ‘drunken dance’ 🍻 – running through shallow water with long strides, staggering sideways, leaping in the air ⬆️, raising one or both wings, and abruptly stabbing at fish 🐠 . Holding its wings over the water while hunting is thought to reduce glare and help the egret more accurately sight 👀 and spear its prey – or maybe it’s to regain its balance, we’re not sure! 🤔
During the 1800s this egret and others were hunted almost to extinction for their beautiful feathers 🪶, used to adorn ladies’ hats and other apparel! Thankfully, two women jump started a conservation movement which put an end to the slaughter. You can learn all about this fascinating history in our webinar: https://bit.ly/Killer-Fashion
Reddish Egrets come in two morphs: the dark morph, with shaggy reddish head 🔴 and neck and slate gray body (more common in the southern U.S. and Mexico); and the more rare white morph, with entirely white plumage ⚪️ (more common in the Bahamas 🇧🇸 and Greater Antilles). Breeding adults of both morphs have a two-toned bill, pinkish at the base and black at the tip.
The Reddish Egret is our rarest and least-studied Ardeid (Family of herons, egrets, and bitterns) – the total population is estimated at only 7,000 to 11,000 birds. It is a Species of Conservation Concern.
✨ Learn more about the Caribbean Waterbird Census (CWC) here and show your support for our citizen science programs like the annual CWC, which gathers critical data to conserve the Reddish Egret and many other threatened birds.
Twelve Whistlers Whistling – West Indian Whistling-Duck
 🎄On the twelfth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, twelve fiddlers fiddling🎶. A kind gesture, but you’d think that after all this time your true love would have recognized your greater appreciation for acapella-style whistling. It’s an acquired taste that only a refined individual like yourself 😎 could truly appreciate. So redirect those fiddlers to the neighbor’s house 🏡 , and head over to a nearby pond to enjoy a musical production 🎭 of Twelve Whistlers Whistling!
🎄On the twelfth day of Christmas, my true love sent to me, twelve fiddlers fiddling🎶. A kind gesture, but you’d think that after all this time your true love would have recognized your greater appreciation for acapella-style whistling. It’s an acquired taste that only a refined individual like yourself 😎 could truly appreciate. So redirect those fiddlers to the neighbor’s house 🏡 , and head over to a nearby pond to enjoy a musical production 🎭 of Twelve Whistlers Whistling!
We thought it fitting to bring our 12 Birds of Christmas to a close with the grace of the West Indian Whistling-Duck 🦆 . You can only hear the hauntingly beautiful calls of this Caribbean bird at twilight 🌅, when the sun begins to dip toward the horizon. West Indian Whistling-Ducks often remain hidden during the day, roosting in mangrove trees 🌳 or other vegetation, and become active at sunset when they feed.
This gorgeous mostly-brown duck was once common, but populations are now very small 📉 and isolated on each island. Destruction of wetland habitats, illegal hunting, and invasive predators (like mongoose) have all contributed to the decline of this species.
The West Indian Whistling-Duck is our flagship species for the conservation of mangroves and wetlands throughout the West Indies! We have a fun curriculum, “Wondrous West Indian Wetlands—Teachers’ Resource Book,” 📖with many hands-on activities 🧩 to learn 🧠 about wetlands and birds, and other resources available on our website. 😉
You can also visit our webpage for more facts, to listen to its song, and free West Indian Whistling-Duck themed activities for adults and children! 😃
And now our 12 Caribbean Birds of Christmas Advent calendar is complete!

 On the most northern islands of The Bahamas, this acrobatic bird can be seen flying low over the roads, fields, and other open habitats. Its ability to twist and turn at the last second is truly impressive – the fighter jets of the bird world. Is it just showing off? No, the Bahama Swallow (Tachycineta cyaneoviridis) is hunting, grabbing unlucky flying insects directly out of the air.
On the most northern islands of The Bahamas, this acrobatic bird can be seen flying low over the roads, fields, and other open habitats. Its ability to twist and turn at the last second is truly impressive – the fighter jets of the bird world. Is it just showing off? No, the Bahama Swallow (Tachycineta cyaneoviridis) is hunting, grabbing unlucky flying insects directly out of the air.

 FOR KIDS: Bahama Swallows feed on insects, swooping through the air to catch them on the wing! Can you help this hungry Bahama Swallow find its way through our maze to to grab some tasty insect food? You can find the correct route here.
FOR KIDS: Bahama Swallows feed on insects, swooping through the air to catch them on the wing! Can you help this hungry Bahama Swallow find its way through our maze to to grab some tasty insect food? You can find the correct route here.