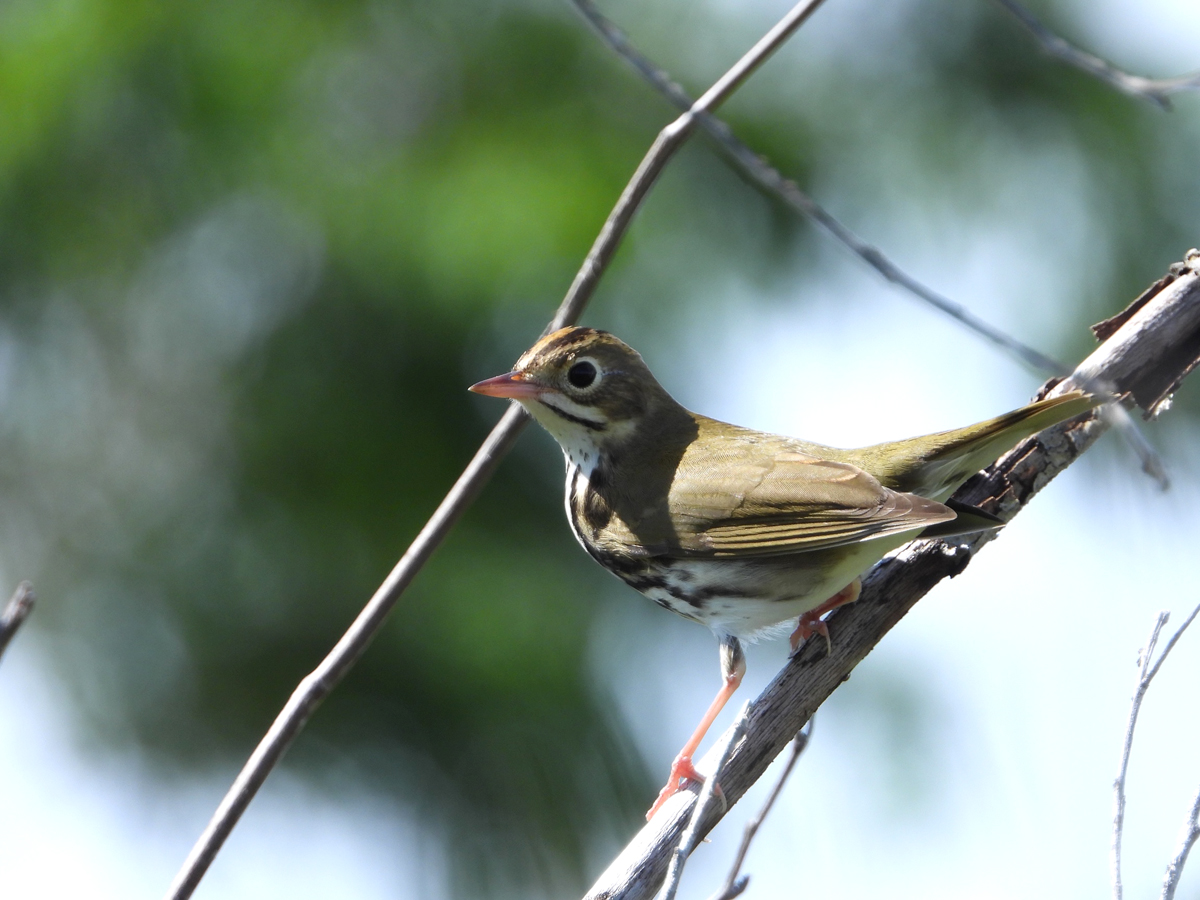
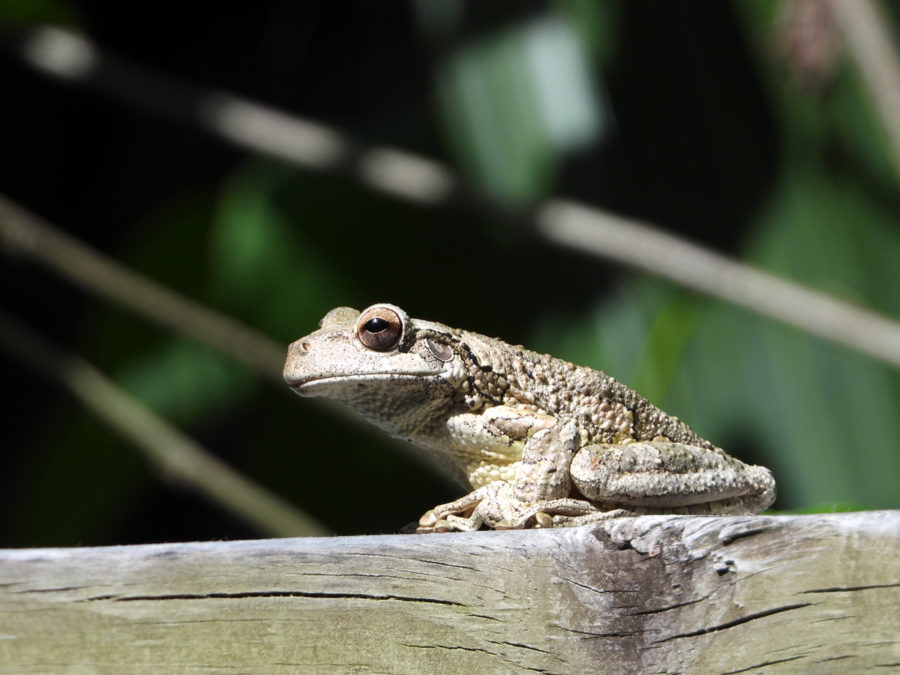
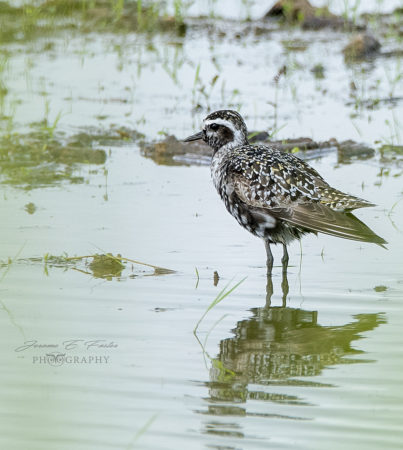
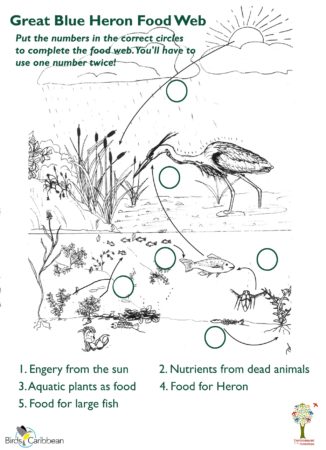
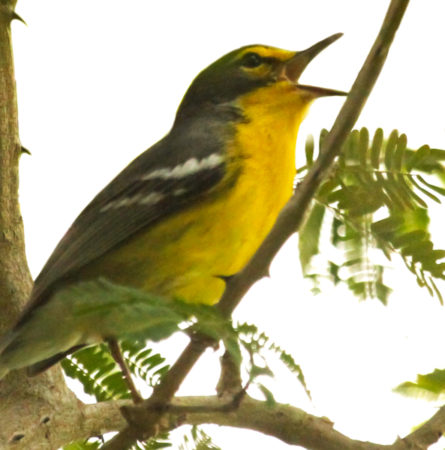
Some warblers are resident in the Caribbean year-round, some spend the whole winter with us and others are brief visitors in Fall and Spring. These beautiful, active little birds can sometimes be a challenge to identify! Gail Karlsson tells us about her warbler encounters in the Virgin Islands and provides some helpful hints for warbler watching.
Migrating warblers generally arrive in the Virgin Islands without great fanfare. They are small and don’t travel in big groups. Then after they land, they hide in the treetops or underbrush. And although they are songbirds, they usually sing to attract mates during their breeding season up north and are pretty quiet when they are here.
I only recently began looking for migrating warblers. It takes a lot of patience, but if you look carefully, you can probably spot some of these tiny travelers.
Adelaide’s Warblers On The Move
The Yellow Warblers I do see near the mangroves are mostly permanent residents. At first, I thought those were the only ones living in the Virgin Islands year-round, but then I heard that some Adelaide’s Warblers had begun to move over to the Virgin Islands from Puerto Rico. I learned about them from Richard Veit, a professor from the College of Staten Island and the City University of New York Graduate Center, who for many years brought students to St. John for a Tropical Ecology course.

The Adelaide’s Warblers were first reported on St. Thomas in 2012. Then in January 2015, Professor Veit and his colleagues counted five near Lameshur Bay, far out on the south shore of St. John. They identified at least three different males that were singing and appeared to have established breeding territories. When they counted again in January 2016, there were eight birds. Soon after that, I trekked out along the south shore trail with a visiting birder friend and we were thrilled to actually see, and hear, a pair of them – although only after we spent quite a long time searching and waiting.

After the Storms
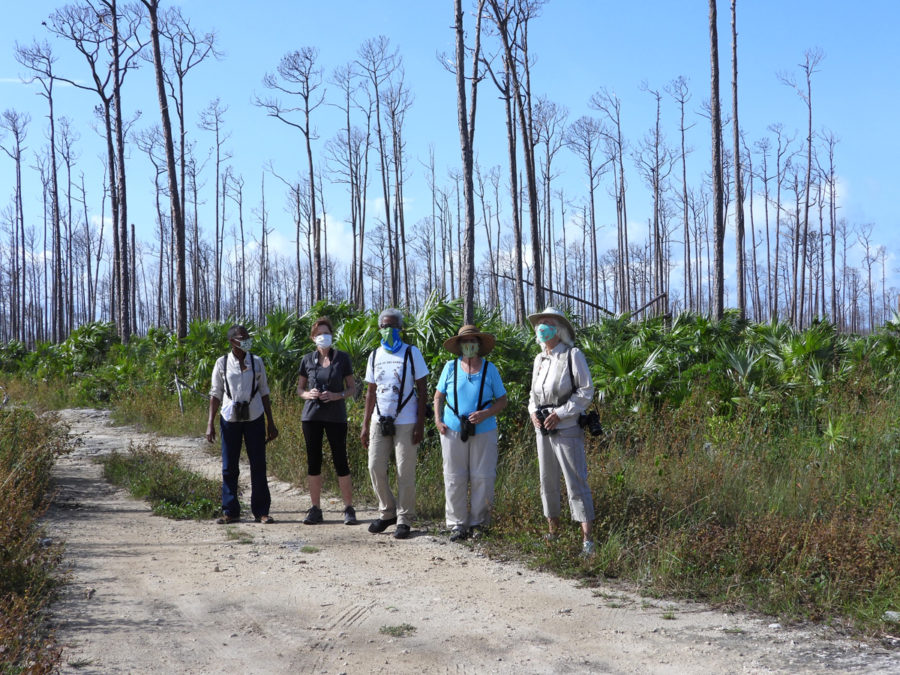
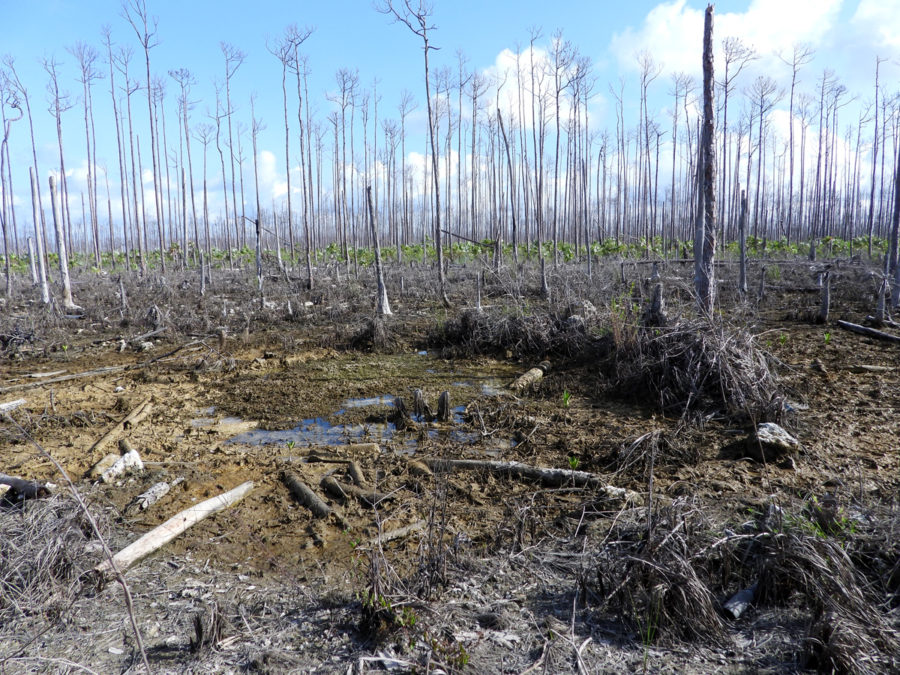
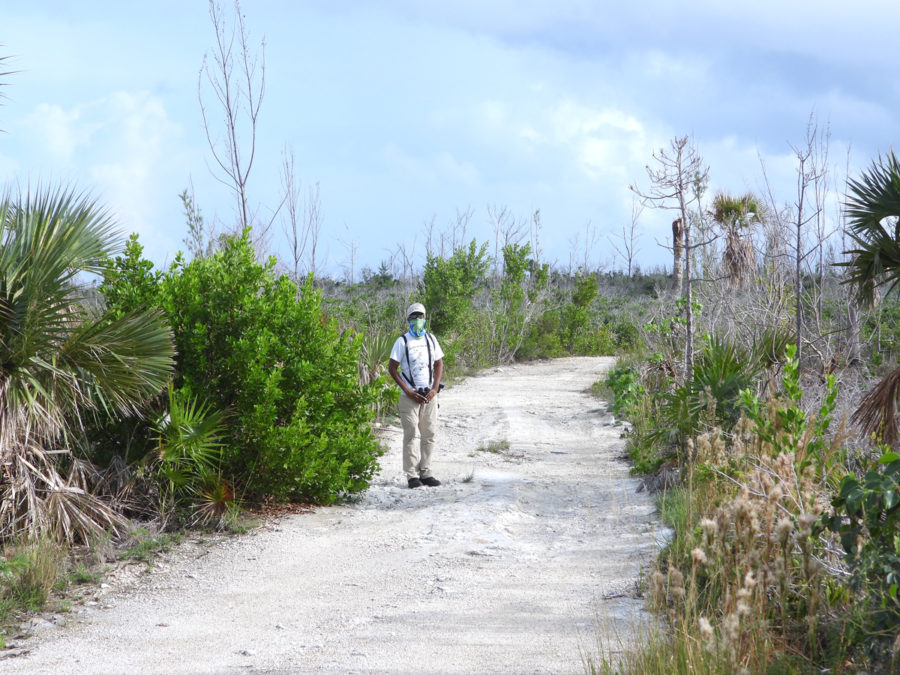
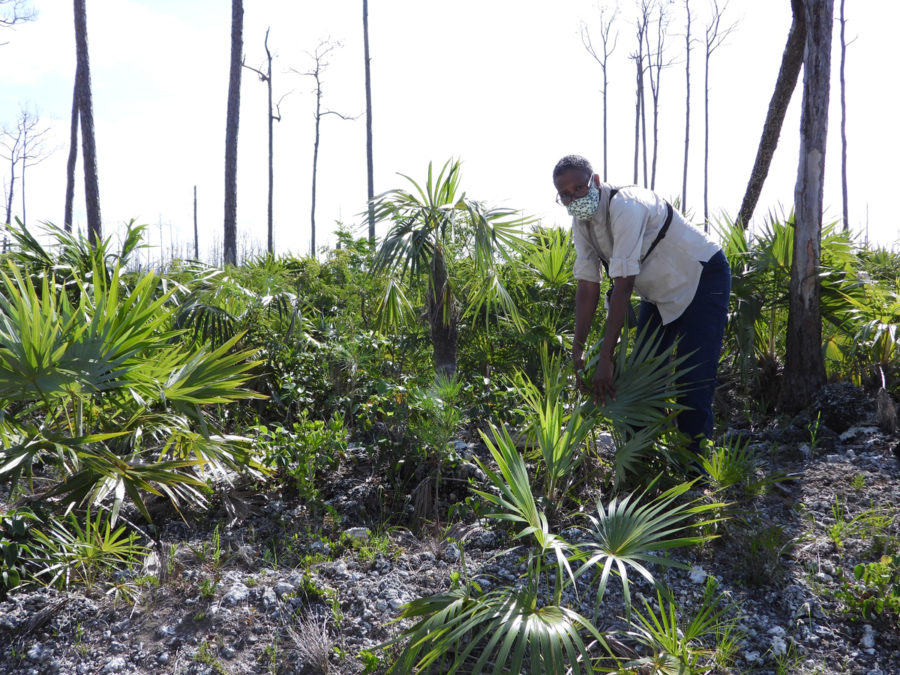
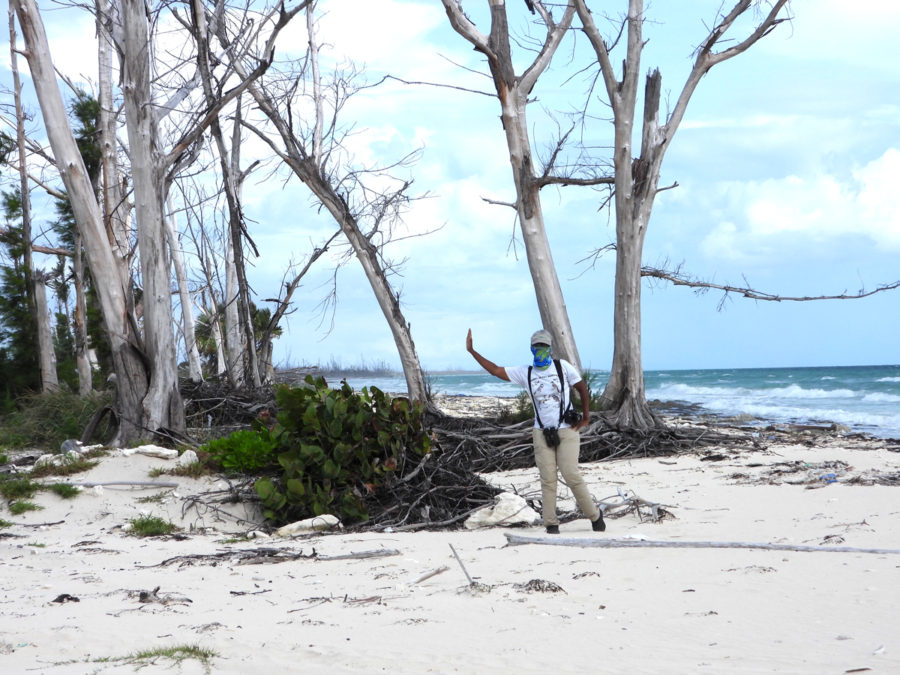
Then in January 2019, I had an unexpected opportunity to go out warbler hunting in connection with a field study to assess the impacts of Hurricanes Irma and Maria, which hit the islands hard in September 2017. Many resident birds were lost during the storms and others went hungry because the trees and plants they relied on as food sources were destroyed. The warbler field study was done by Robert Askins, a researcher from Connecticut College, and his colleague David Ewert from Michigan, who had done previous studies of birds in the Virgin Islands National Park on St. John.
When I went along on one of the early morning bird hunts, I was surprised that the experts were not actually looking for the warblers – just listening.
The Elusive Warblers: Keeping Ears and Eyes Open
Although warblers don’t usually sing unless they are breeding, they do make small ‘chip’ sounds to communicate with each other. I learned that there are slight differences in the ‘chips’ produced by different birds, which experts can recognize. I couldn’t do that, so I was mostly looking around for movement in the trees, but I did get interested in spotting warblers.
I started paying more attention when I heard little ‘chip’ sounds in the trees and spent more time quietly waiting for the birds to show themselves. After a while I began to be able to identify some of them by how they moved around.
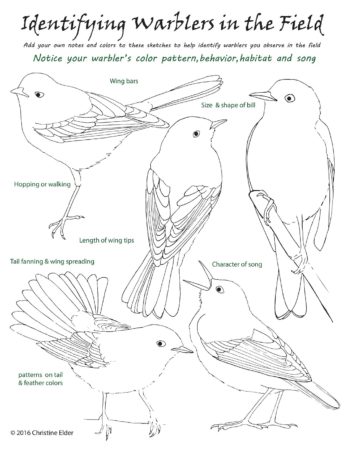
It also helps to learn more about which types of migrating warblers visit the Virgin Islands, and what they look like.
Black and White Warblers generally crawl along a tree’s trunk or branches, looking for bugs.
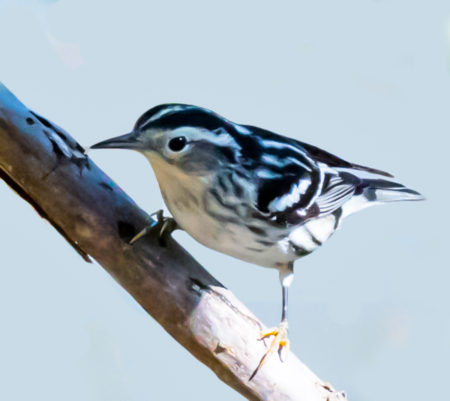

American Redstarts flit around in the tops of trees, using their bright tails to scare up insects.
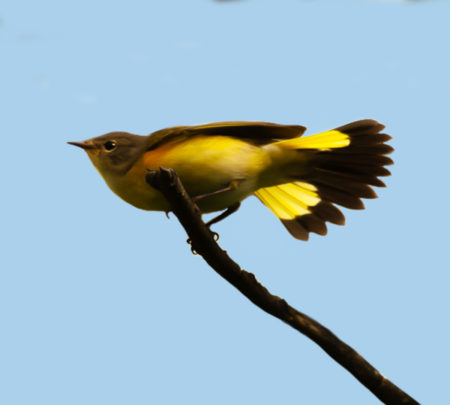

Northern Parulas often quietly chase moths and other bugs in upland trees.

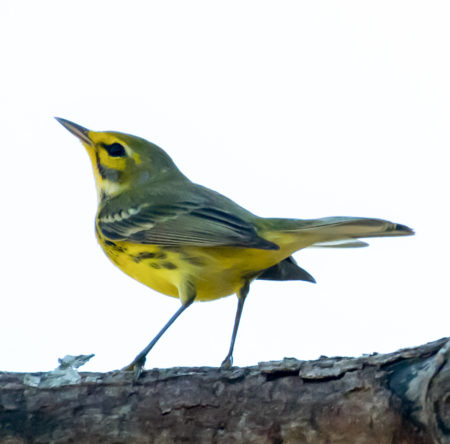
Occasionally I will see a bright, yellow Prairie Warbler near the mangroves, bobbing its tail as it hunts for insects.

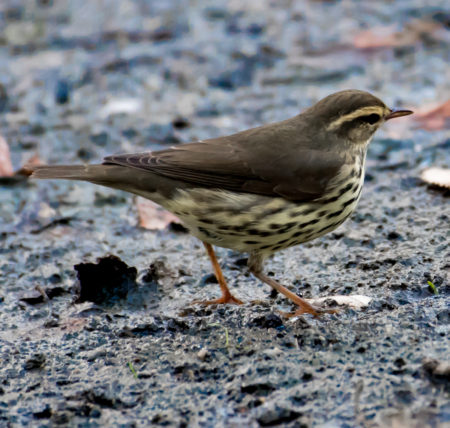
Northern Waterthrushes creep around low down in the wetlands hunting for insects and small crustaceans. They are usually well-concealed but announce their presence by making really loud ‘chips’.

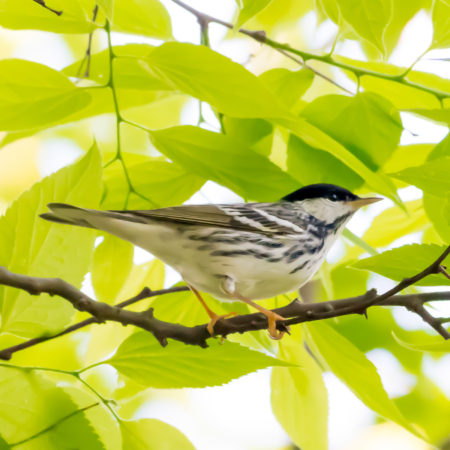
The Blackpoll Warblers’ Exhausting Journey
Recently, I was also excited to spot a few Blackpoll Warblers. Warblers generally move north in the spring to take advantage of the seasonal burst of plants and insects to feed their young. The Blackpolls go really long distances – some flying up from South America and then across the northern United States and Canada, as far west as Alaska. In breeding season, the male Blackpolls have distinctive black caps, and black and white streaks on their bodies.

In the fall, the Blackpolls look totally different. The males have no caps, and they all have a dull olive-greenish color.

On their way back to South America in the fall, the Blackpolls gather along the northern part of the east coast (a 3000-mile trip for the ones in Alaska). They wait for a night when there is a favorable tailwind blowing out of the northwest, and then take off. They head away from the coast far out into the Atlantic Ocean, flapping their tiny wings about 20 times per second. After a few tiring days, they get far enough south to be pushed back eastward towards South America by the trade winds.
A few Blackpolls sometimes stop in the Virgin Islands during their fall migration, though they don’t usually stay long. What a thrill to see them on their journey.
The Importance of Native Trees
For people living in the Caribbean, one of the best ways to be able to see wintering warblers is to preserve native trees that support a variety of insects. Non-native plants are often unattractive to local insects, and so are not useful for bug-eating birds. Also, cutting down trees, and using pesticides can eliminate important food supplies for birds.
It can be frustrating to try to see the visiting warblers. But I like the way that looking for birds gets me out exploring – walking in the woods or along the shoreline, feeling connected to the great rhythms of nature, and forgetting about the day’s troubles and turmoil for a while.
________________________________________
Gail Karlsson is an environmental lawyer, writer and photographer – author of The Wild Life in an Island House, plus the guide book Learning About Trees and Plants – A Project of the Unitarian Universalist Fellowship of St. John. She writes frequently about connecting with nature, including for the St. John Source. See gvkarlsson.blogspot.com and uufstjohn.com/treeproject. Follow her on Instagram @gailkarlsson.
This story is adapted in part from a recent St. John Source article.