Celebrate World Migratory Bird Day (WMBD) with us in 2022! This year’s theme is “Dim The Lights for Birds at Night”. Have fun learning about a new migratory bird every day. We have colouring pages, puzzles, activities, and more. Download for free and enjoy nature with your family at home.
Migratory Bird of the Day: Bobolink
Be on the lookout for migratory Bobolinks! Known as the “backwards tuxedo bird” or “skunk bird,” breeding males have a bold black plumage with a white rump and soft yellow nape. However, females and non-breeding males have a more subtle beauty, boasting a buffy yellow-brown plumage with fine brown streaking all over the body and a distinct stripe through the eye. Be sure to look for their distinct spikey tail. It’s speculated that the Bobolink may have received their unique name from the poem “Robert of Lincoln” by American poet William Cullen, as the sight of large flocks of these birds was likely the inspiration for the poem.
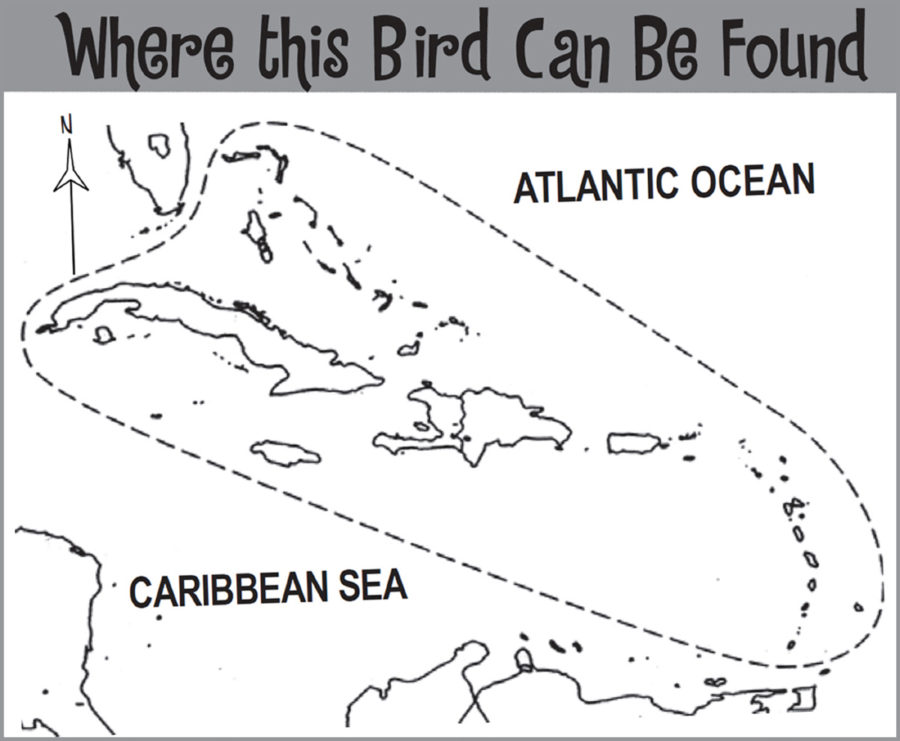
During migration, Bobolinks can often be found in large flocks. They are quite an impressive migrant, known to log an approximate 20,000 km round trip from geolocater data (birds tagged with small backpacks that can log their location and tell us more about migratory movements). Bobolinks breed in the grasslands of the Northeastern US. They follow the Eastern flyway and migrate through the Caribbean, taking an extended stopover in Venezuela before continuing south to their overwintering grounds in Argentina, Paraguay, and Bolivia.
Boblinks have been reported to have a high site fidelity, both to their breeding and overwintering grounds. Some farmers in South America have reported having large flocks of Boblinks in their rice fields for 50 years!
In the early 20th century these birds were so numerous migrating through the Caribbean that non-stop flights from Jamaica were termed “Bobolinks!” In the Caribbean, Bobolinks can be found during migration in the Bahamas, Jamaica, and many of the lesser Antilles. Banding data has shown us that during migration, especially before crossing the Caribbean, these birds can increase their body weight by up to a third, going from 38g to 50g!
Unfortunately Bobolinks face a variety of threats on their migratory journeys. In the US, Argentina, and Bolivia their affinity for grasslands has labeled them as an agricultural pest. This has led to birds being shot or poisoned to save crops. On their breeding grounds birds may abandon nests due to mowing of agricultural lands. In Jamaica and Cuba, these birds are often caught for the domestic and international caged bird trade, and are sometimes even eaten. These threats mean the Bobolink is a Species of Conservation Concern in eight states in the US and they are protected under the US Migratory Bird Treaty Act. Protection of grasslands has helped their breeding populations as has banning of dangerous pesticides in Bolivia and Argentina. Learn more about this species, including its range, photos, and calls here.
Colour in the Bobolink
Download the Migratory Birds of the Day Colouring Page! Use the picture above and the photos on this page as your guide, or you can look up pictures of the bird online or in a bird field guide if you have one. Share your coloured-in page with us by posting it online and tagging us @BirdsCaribbean #WMBD2022Carib
Listen to the calls of the Bobolink
Bobolinks have a distinctive “pink ” call they use all-year round. You might also hear the rambling, metallic sounding, multi-note male song.
Puzzles of the Day
Click on the images below to do the puzzle. You can make the puzzle as easy or as hard as you like – for example, 6, 8, or 12 pieces for young children, all the way up to 1,024 pieces for those that are up for a challenge!


Activity of the Day
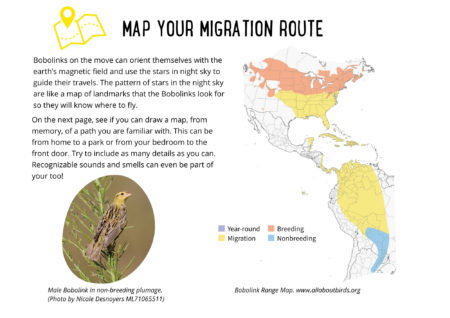 FOR KIDS: Bobolinks on the move can orient themselves with the earth’s magnetic field and use the stars in night sky to guide their travels. The pattern of stars in the night sky are like a map of landmarks that the Bobolinks look for so they will know where to fly. Bobolinks use the stars in the same way we might look for familiar buildings, trees on landscape features like hills and rivers to find our way from one place to another. In fact the stars are just like these types of landmarks for Bobolinks! Think about a path you are familiar and see if you can draw a map, from memory, of this route. You could include sounds and smells as well as the things you see along the way!
FOR KIDS: Bobolinks on the move can orient themselves with the earth’s magnetic field and use the stars in night sky to guide their travels. The pattern of stars in the night sky are like a map of landmarks that the Bobolinks look for so they will know where to fly. Bobolinks use the stars in the same way we might look for familiar buildings, trees on landscape features like hills and rivers to find our way from one place to another. In fact the stars are just like these types of landmarks for Bobolinks! Think about a path you are familiar and see if you can draw a map, from memory, of this route. You could include sounds and smells as well as the things you see along the way!
FOR KIDS AND ADULTS: Neonicotinoids are a type of pesticide and this group of chemicals are widely used in America. They can be found in a large proportion of corn crops groups in the US and nearly half of soybeans. Neonicotinoids can impact on the critical functions of songbirds, including effecting their metabolism, reproduction and migration patterns. Given that they are so widely used these effects on songbirds are deeply worrying. You can read more in the article below, about how pesticide use is affecting songbirds, including the Bobolink, in North America.
Enjoy this video of a male Bobolink foraging in the wild!