It was an extraordinary year. But then, so was 2020! Despite the ongoing roller coaster ride that was the COVID-19 pandemic, BirdsCaribbean pressed on. While some activities were necessarily curtailed, with our ever-enthusiastic partners we “pivoted,” adapted to the changing circumstances, and overcame obstacles. We had some great successes. We also turned to highlighting some pressing issues impacting our Caribbean birds. Now, we are looking forward to an exciting 2022, full of potential and possibilities!
 We are feeling very positive about this new year. The theme of our upcoming conference in Puerto Rico (June 27 to July 2), which we are co-hosting for the first time with the American Ornithological Society (AOS), is “On the Wings of Recovery: Resilience and Action.”
We are feeling very positive about this new year. The theme of our upcoming conference in Puerto Rico (June 27 to July 2), which we are co-hosting for the first time with the American Ornithological Society (AOS), is “On the Wings of Recovery: Resilience and Action.”
This theme reflects the focus of our activities in the past year, supporting our partners as they work on solutions to the many challenges facing the region’s birds. We are also looking forward to hosting workshops in the Dominican Republic and The Bahamas, on Landbird Monitoring and Bird Banding, respectively.
In case you missed it, here’s an overview of BirdsCaribbean happenings in 2021:
It was a “quiet” year, but…

Thankfully for the islands, the hurricane season was not as devastating as in previous years, although climate change is still with us. Year after year, the region continues to suffer from droughts, coastal erosion, and floods after heavy rains, damaging habitats and creating havoc in communities. However, there was still some unexpected drama this year.
The explosive eruptions of La Soufrière, a volcano in St. Vincent, began on April 9th, 2021, and continued spewing volcanic ash and debris into the atmosphere for weeks – displacing thousands and blanketing forests and towns in many inches of volcanic ash. Although it has now quietened down (its eruptive phase was declared over at the end of November, 2021) there was considerable damage to trees and river valleys from pyroclastic material, rocky debris and mudflows.
In the wake of the destruction, concerns for the St. Vincent Parrot and several other endemic bird species rose and we were thankful for the valiant efforts of the St. Vincent and the Grenadines Forestry Department. With generous donations from friends and donors to the BirdsCaribbean fundraising site, we were able to ship a range of supplies to the Department, including field equipment, food, veterinary supplies, and much more. We also supported intensive surveys of the St. Vincent Parrot by Forestry staff in December, 2021 – more news on their status soon!
A Turkey Vulture costume, the biggest Big Day, and CWC was busy too
As usual, bird festivals were important days in our calendar. Island residents hosted at least scaled-down activities – whether virtual, in person, or a “hybrid” mixture, since COVID regulations varied from time to time.

World Migratory Bird Day (WMBD) in Fall, when our beautiful “winter visitors” start to appear in gardens, fields and forests across the Caribbean, is always an opportunity for fun activities, especially with young people. This year’s theme, “Sing, Fly, Soar Like a Bird” inspired bird walks, field trips and an exciting Bird Costume Party, won by creative schoolchildren in Cuba. The winning Turkey Vulture costume was stunning! Many thanks to Environment for the Americas for assisting with educational materials.
Our Caribbean Endemic Bird Festival (CEBF), which we have hosted for the past twenty years, is always a delight. 2021 did not disappoint. After all, we have no less than 171 endemic species to choose from! The theme “Sing, Fly, Soar Like a Bird” provided ample opportunities for fun activities and important learning through webinars, birding field trips, and activities and online resources for families and youth to celebrate. Check out the exciting webinars here! Our partners shared what the theme meant to them in short inspiring videos – these can be viewed here.
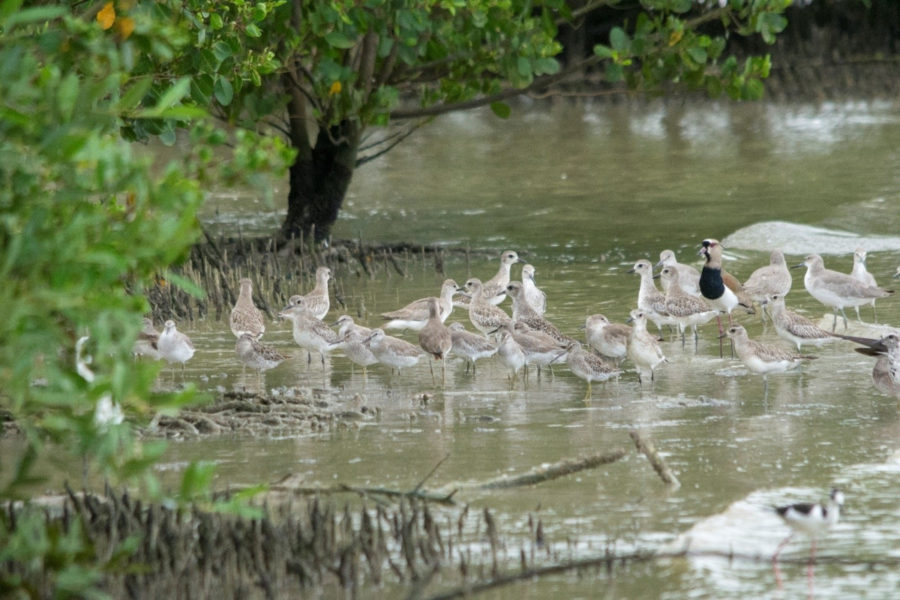
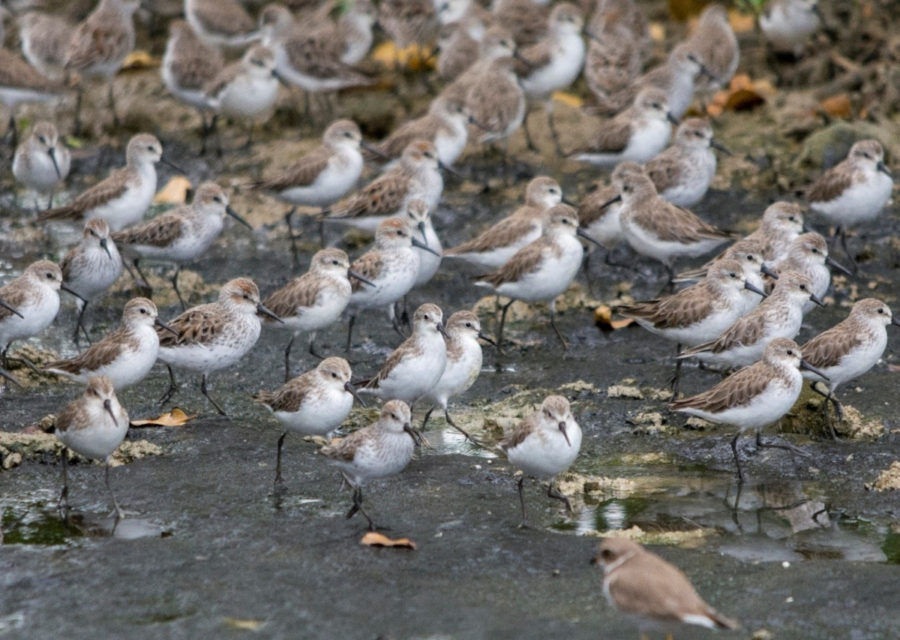
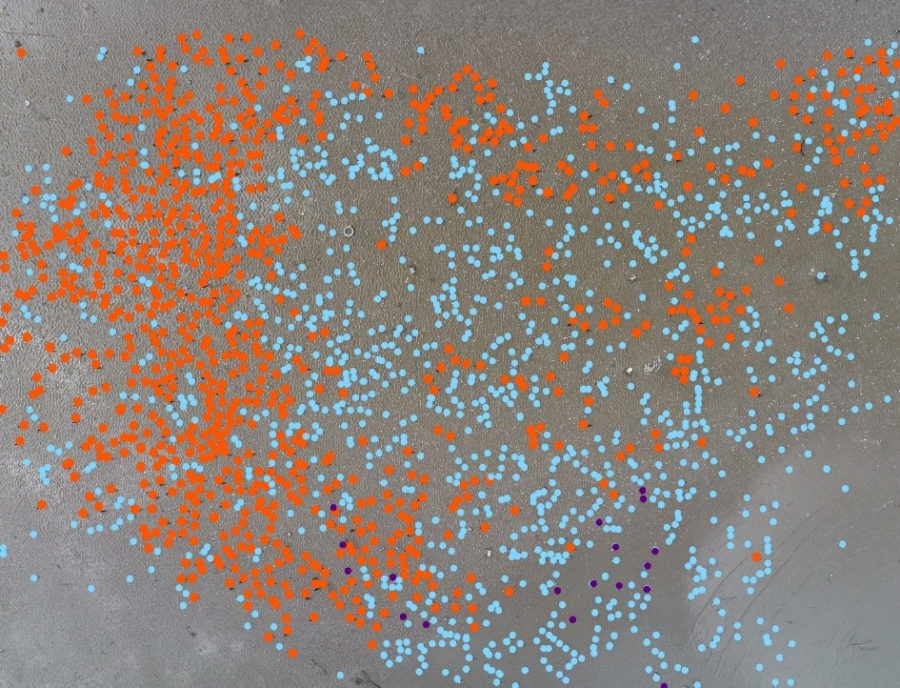
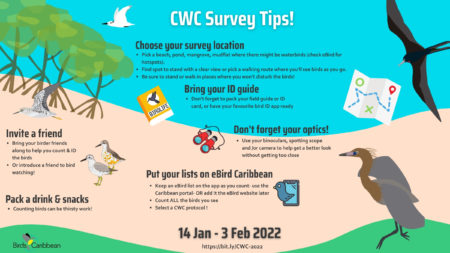
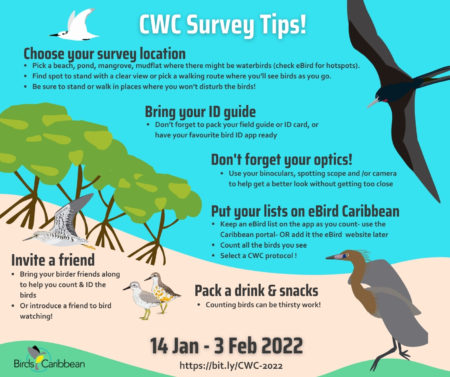
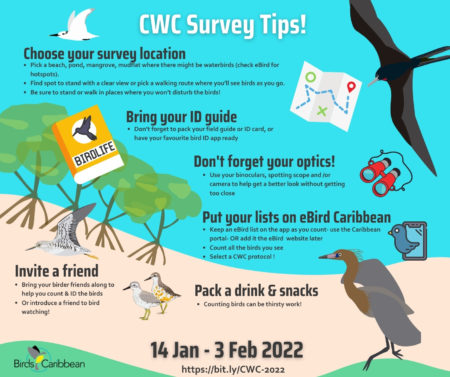
The 12th annual Caribbean Waterbird Census (CWC) was another important activity, which was highly successful. From mid January to early February, birders fanned out across wetlands and beaches to record their sightings on eBird Caribbean. From the offshore islands of Venezuela to the wetlands of Kingston Harbour, Jamaica, there was a great turnout of birders. Anguillan partners were excited to spot Piping Plovers, while in Antigua, a young birding group participated in a “Mask-erade.”
We did mention successes, didn’t we? Global Big Day 2021 (Saturday, May 8) was – well, big! Close to 2,000 checklists were submitted from the Caribbean – a big jump in participation. 364 species were spotted, beating last year’s record. Cuba, Puerto Rico and the Bahamas were stars, and fifteen teams participated, raising funds for Motus bird monitoring stations. Some wonderful photos were taken of birds and people, enjoying the day; take a look here at the winners of our Photography Awards.
An exciting project is about to unfold…
Earlier this year, we announced our plans for a new bird monitoring initiative, the Caribbean Motus Collaboration, to set up a Motus Wildlife Trafficking System that will use nano-tags tracked by receivers to gain valuable data on the movement of birds across our region. We are grateful to Birds Canada and the Northeast Motus Collaboration for their support. For full details and if you are interested in contributing in any way, please complete a short survey or make a contribution here.
A wealth of online material – yes, we went virtual again

To enhance these programs and special calendar events, and also to boost our advocacy for birds, we were very busy throughout the year designing and producing a whole range of online products. In 2021, we again broadcast virtually “From the Nest” with an Endemic Bird of the Day for the CEBF, accompanied by related puzzles, games and coloring pages. Our very first “Bird Zine” contest garnered some beautiful, artistic products from contestants in various age groups, with winners from Cuba, Puerto Rico, and Trinidad and Tobago. For the Caribbean Waterbird Census we started off with no less than three webinars, helping us to identify tricky species and with an additional webinar on Puerto Rican waterbird species.
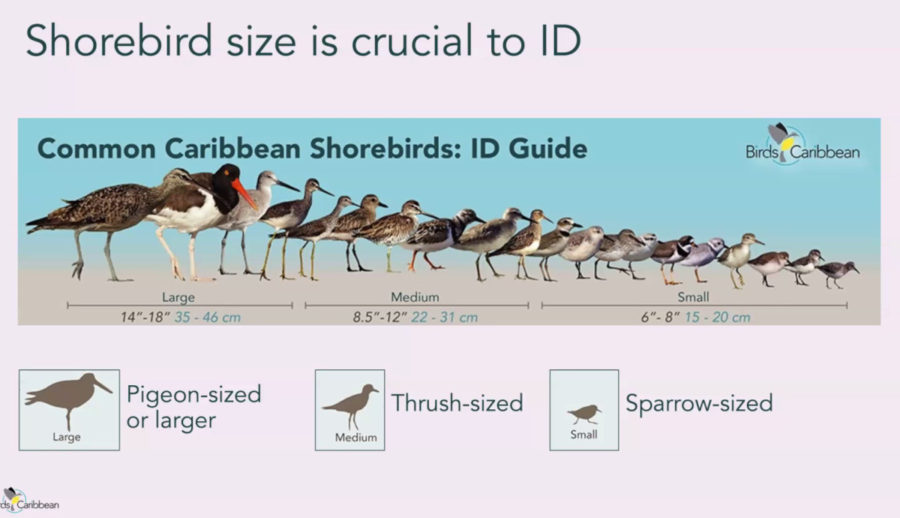
For the 2021 Caribbean Waterbird Census, we gave webinars on how to participate in the CWC, including presentations on using eBird Caribbean and Merlin, how to do a CWC count, and how to identify waterbirds and shorebirds – always challenging! Check out our helpful webinars on our Youtube channel CWC playlist.
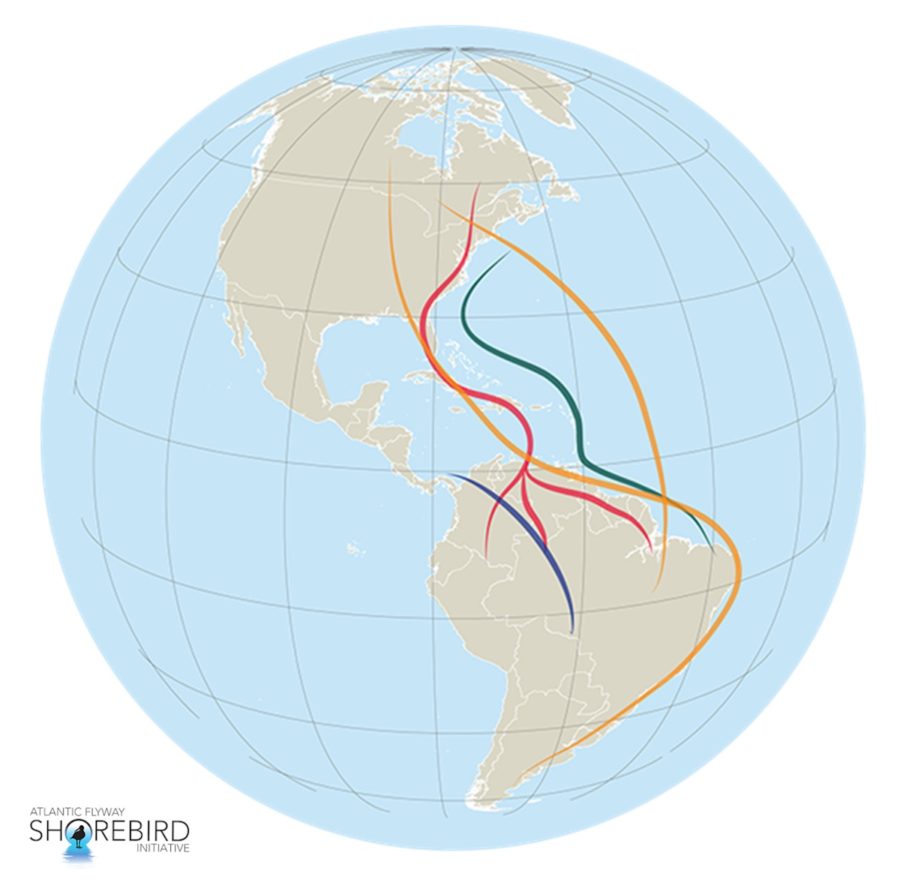
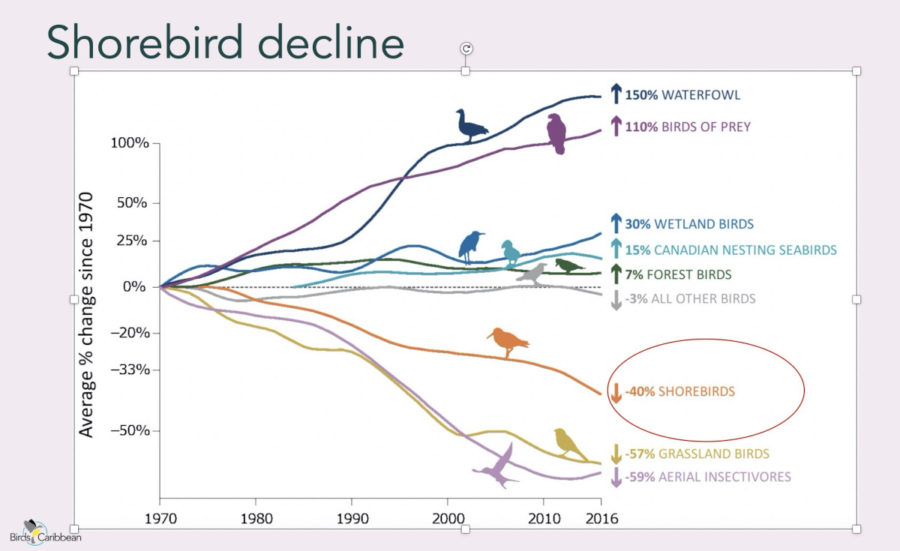
For World Migratory Bird Day, we produced a series of four videos highlighting our migratory shorebirds, many of which are endangered. One species, the Lesser Yellowlegs, is in particular trouble, with a drastic decline in numbers since the 1970s. At a free webinar on October 8, wildlife biologist for the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Migratory Bird Management Program Laura McDuffie explained the work she and colleagues are doing to track, monitor and gain more information on these vulnerable birds.
All our videos may be viewed on our YouTube channel. Take a browse through!
And we met online, too…
A major highlight of our year was the opportunity to present at the 2021 AOS Virtual Meeting, from August 9 – 13. BirdsCaribbean was thrilled to present a three-part symposium entitled “Resilient Caribbean Birds – Surviving and Thriving in a Challenging World,” in which we highlighted recent avian research and conservation projects in the region, on August 11 and 12. Our presentations were well attended and online networking and information sharing took place.
And then, to business. Our General Business Meeting on October 28 had over 80 participants and lasted for over two hours (there was a lot to tell our members and supporters about!) providing a comprehensive update on BirdsCaribbean’s activities.
One memorable online event was the Seabird Fest on December 2, organized by our dynamic Seabird Working Group. The meeting provided a thorough update on the group’s impressive activities, from the Isla Contoy National Park (Island of Birds) off the Yucatan peninsula to Bermuda and the Cayman Islands – and all islands in between. There are 20 resident seabird species in the Caribbean, not all regularly monitored. The hope is to organize a big seabird monitoring effort in 2023. While it faces challenges, we applaud this group’s work. If you would like to know more, sign up for their recently launched newsletter!
Our advocacy for birds continues…
Our focus on shorebirds tied in with ongoing concerns among ornithologists and bird lovers regarding the hunting of these migratory gems on the islands of Guadeloupe, Martinique, and to a lesser extent Barbados. In a short video “Caribbean Shorebirds Under Fire” (available in English, French and Spanish here) that is at times distressing to watch we sought to explain this complex issue. We continued to support our partners’ efforts to have as many species as possible protected and to reduce this devastating harvest of endangered birds, through email petitions to the French authorities.

Many migratory species are also under threat on the island of Cuba, due to the illegal capture and sale of wild birds as they arrive on the island in the autumn months. Endemic and resident species are also targeted by trappers. BirdsCaribbean is extremely concerned at the dramatic increase in the trafficking of a range of species, both at home and extending overseas. We highlighted this growing concern recently in our investigative report, urging Cuban authorities to enforce wildlife protection laws. We are raising funds to help our colleagues combat this problem and we need your support! We will continue to shine the spotlight on these and other issues that are affecting our birds negatively.
We have had a frantically busy year, as you can see. Despite the difficulties of the pandemic, with the support of our wonderful donors and the boundless enthusiasm, dedication, and hard work of our partners on the ground, we feel a sense of achievement, and look forward to what 2022 will bring.
Wishing you all a happy, peaceful and prosperous New Year!
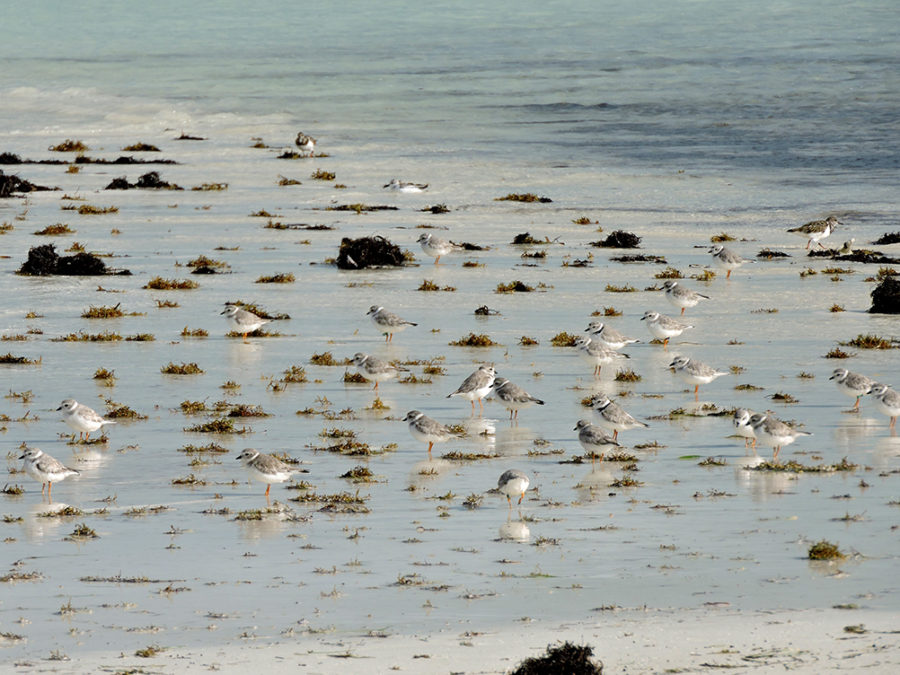
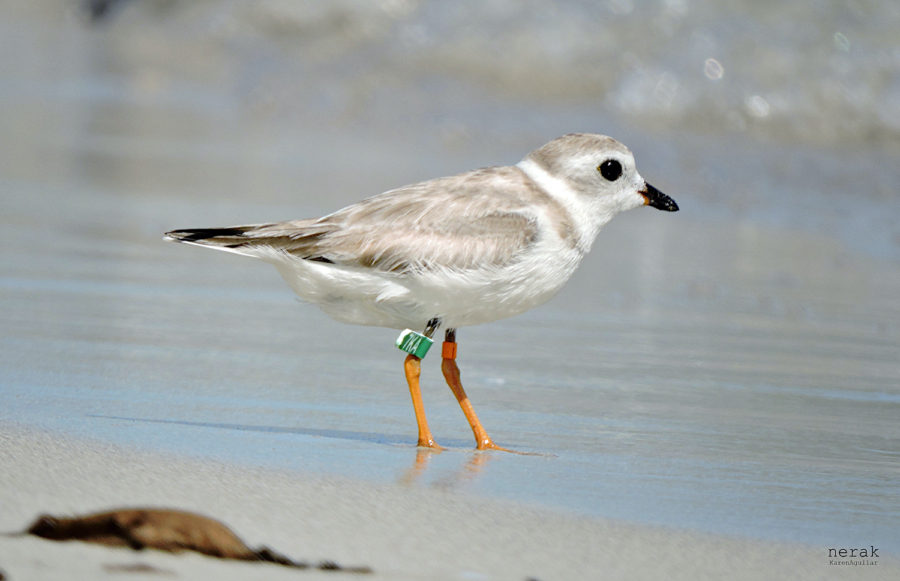
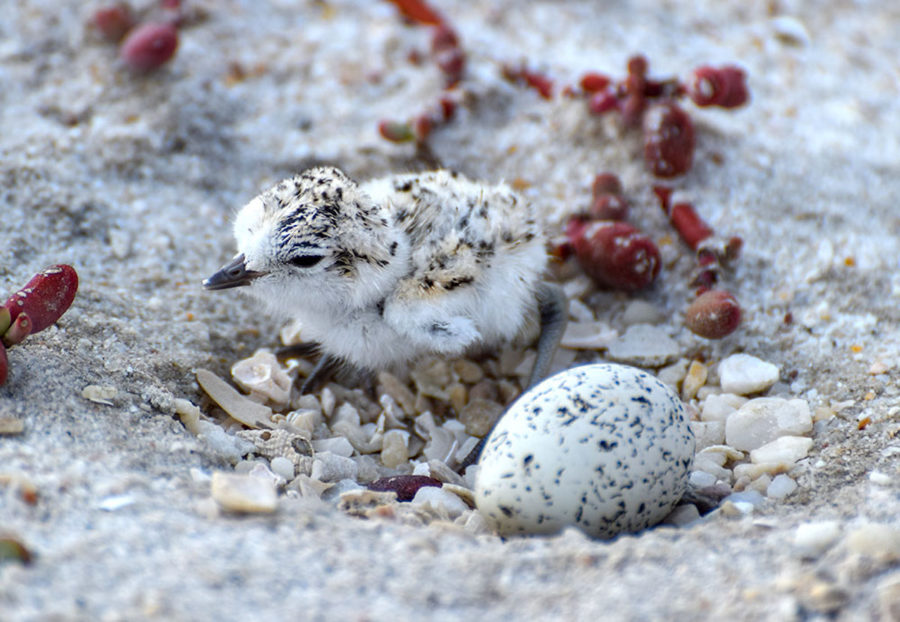
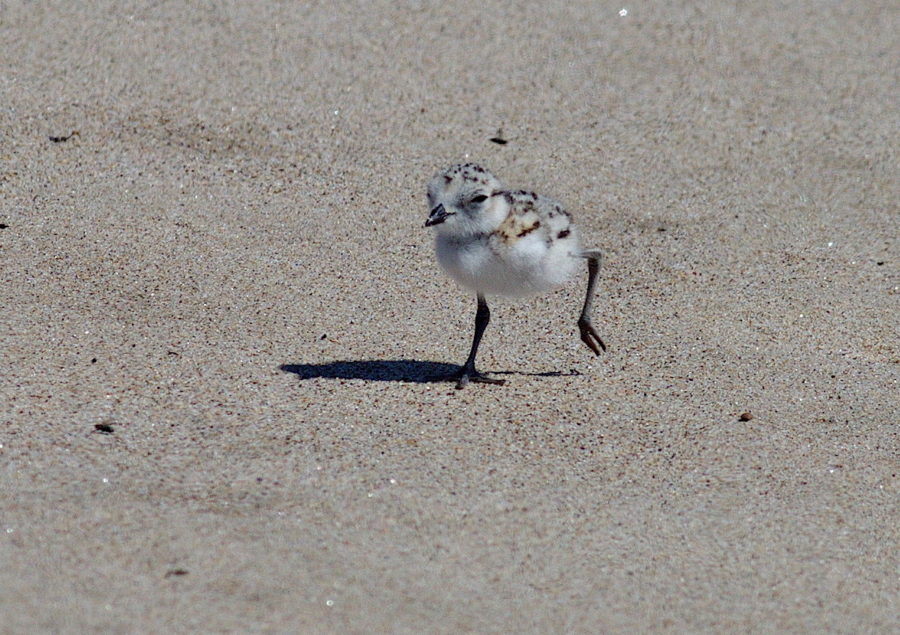
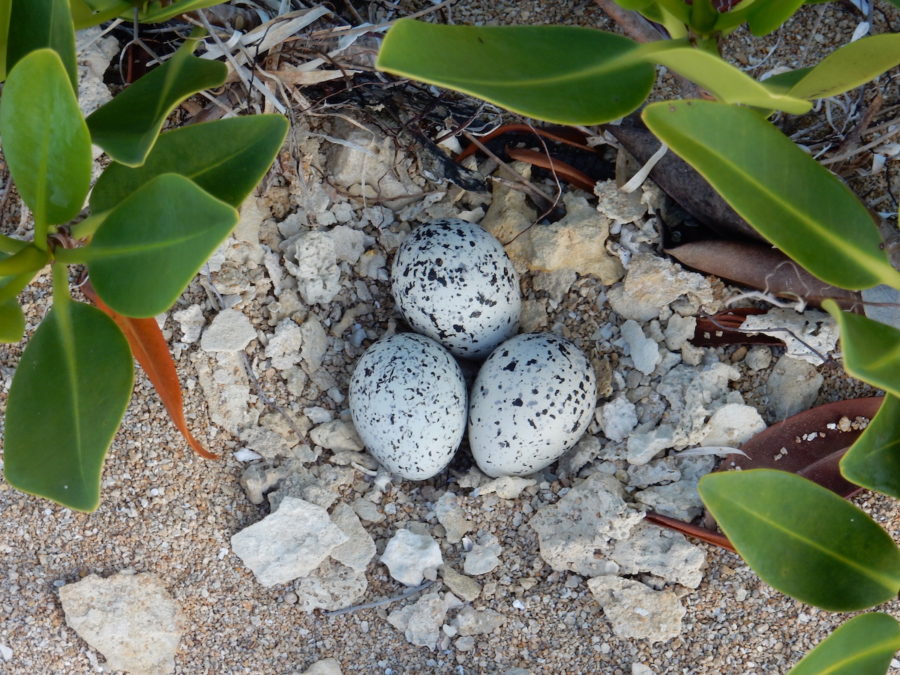
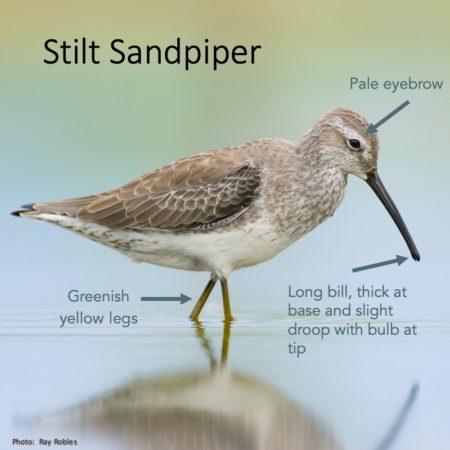
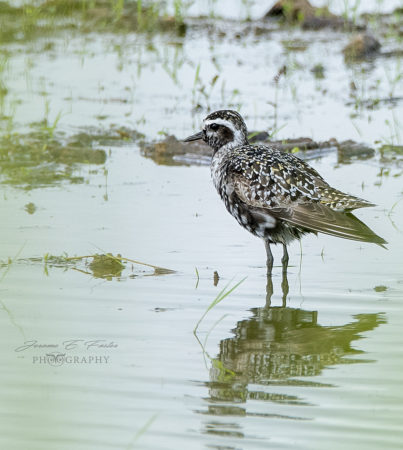
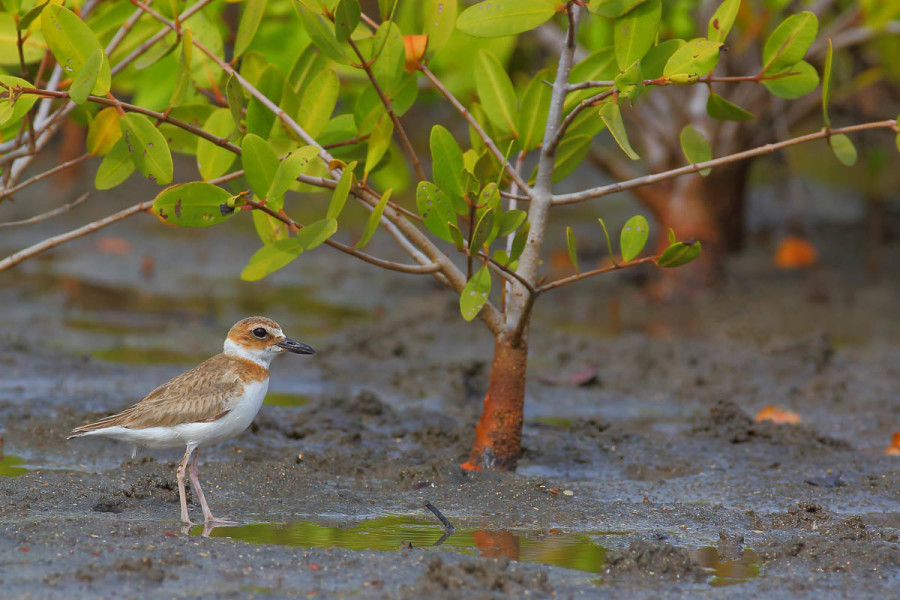
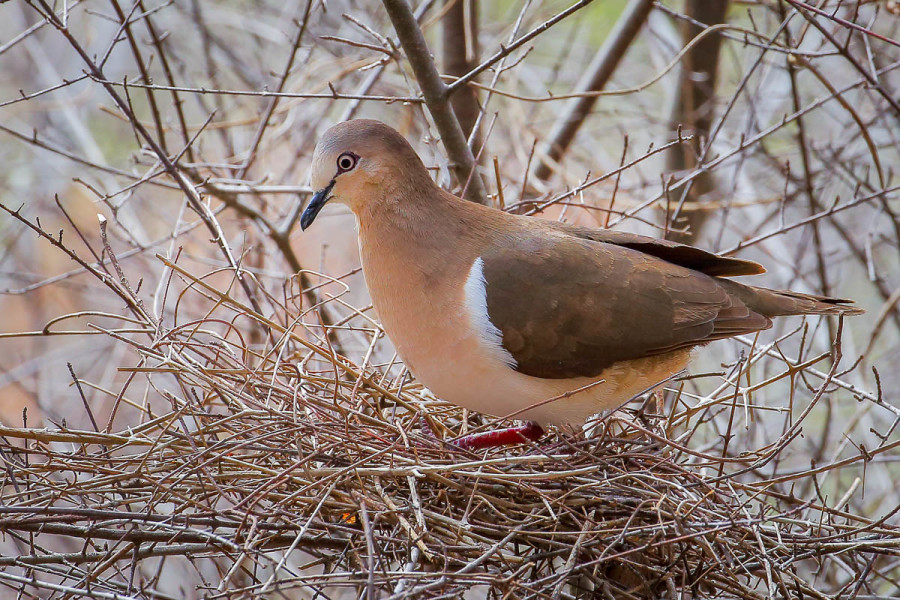
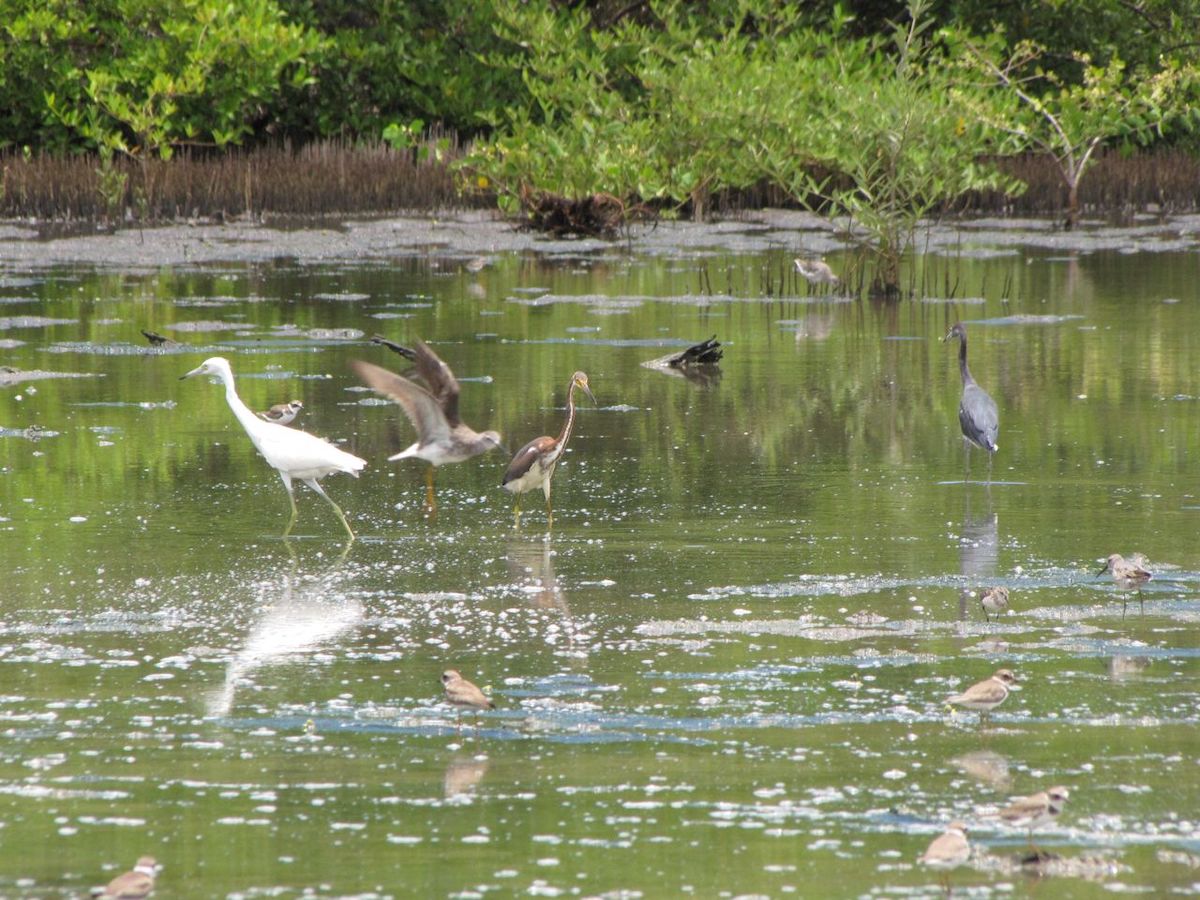
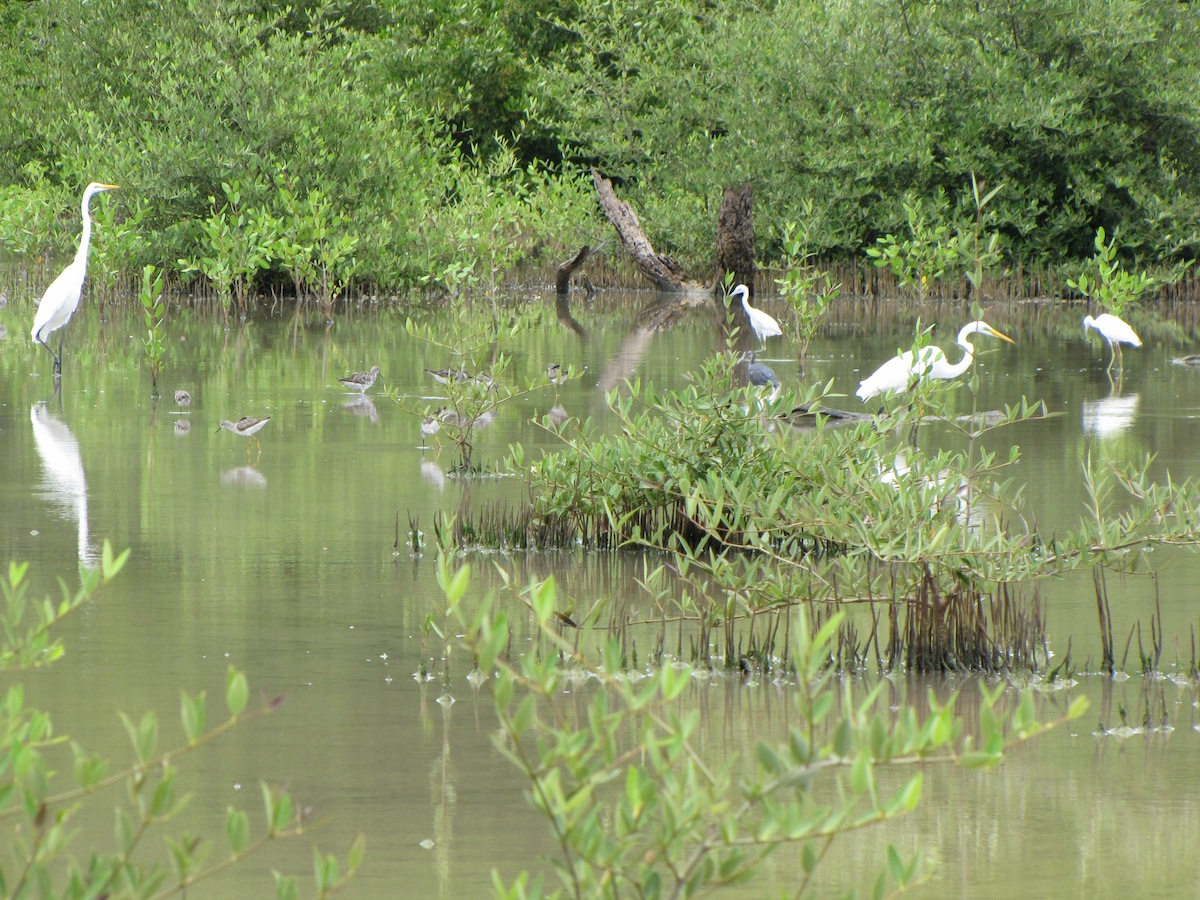
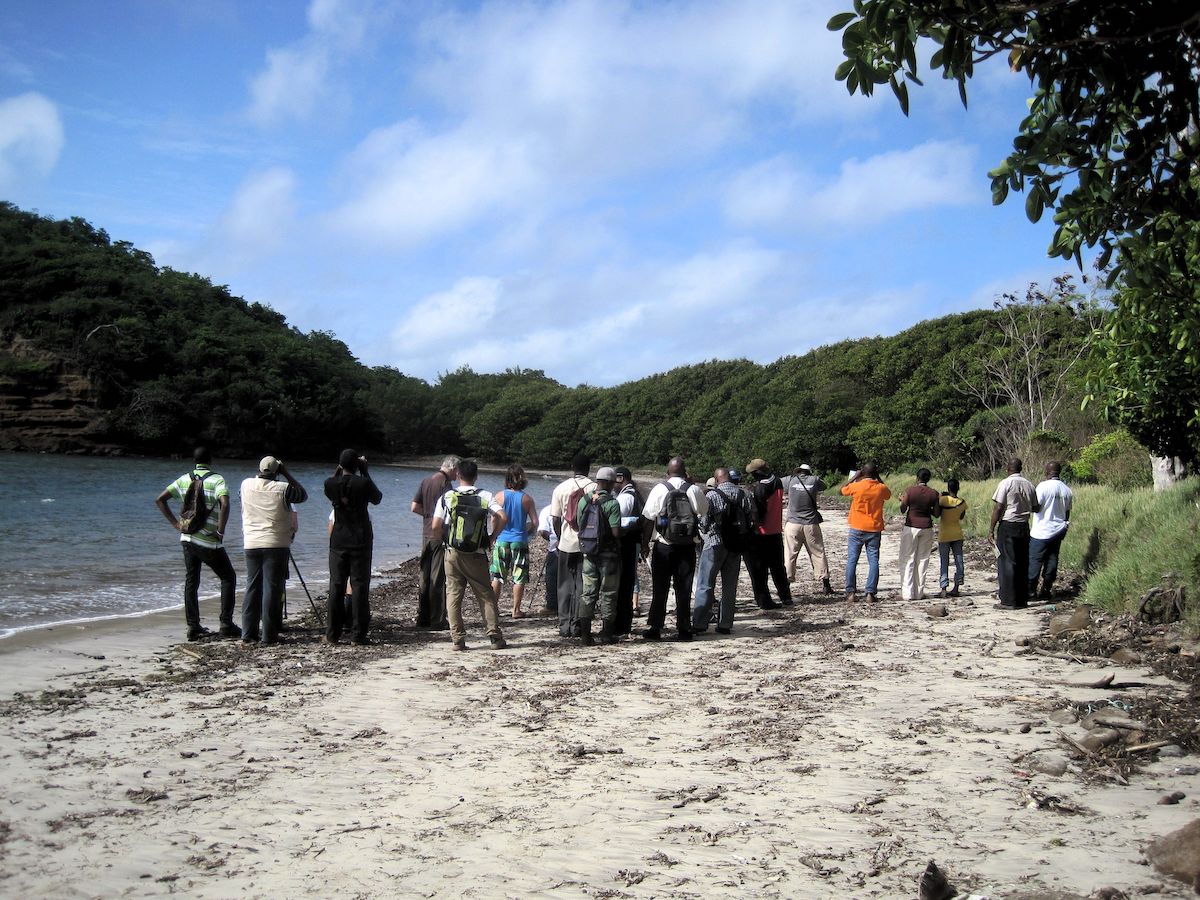
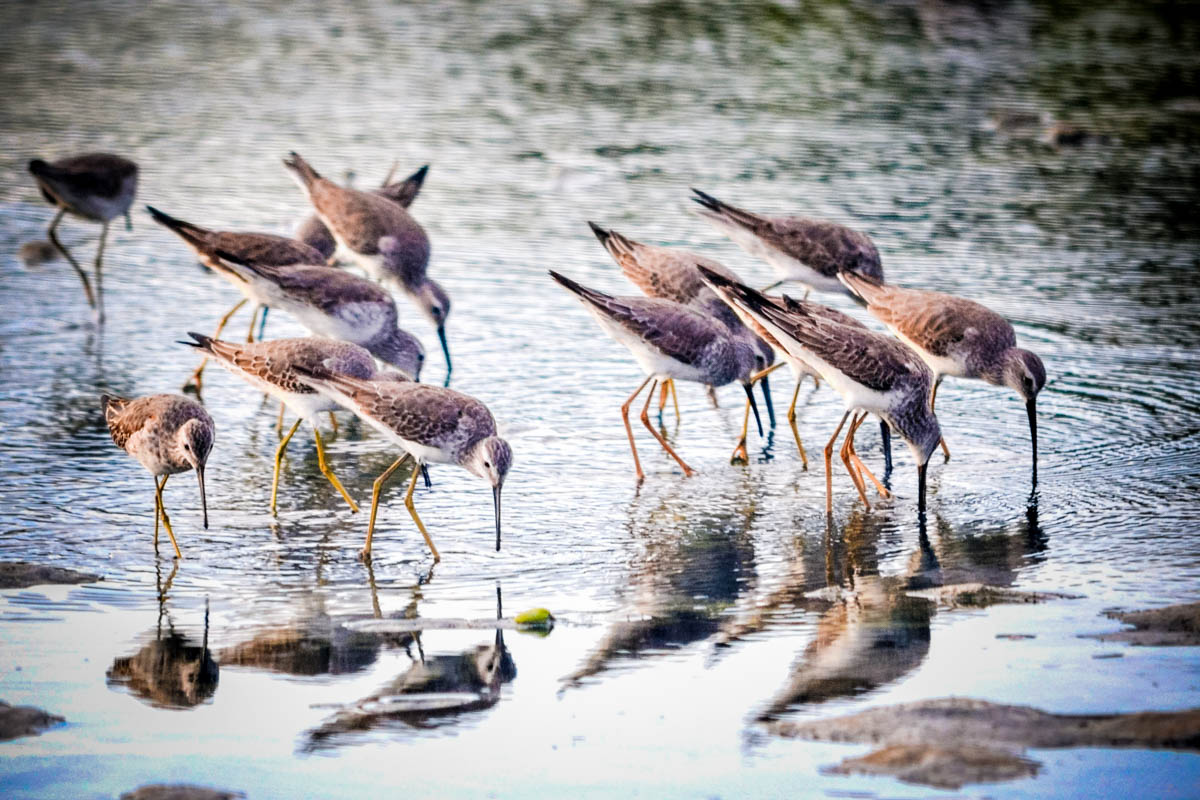























































































































































































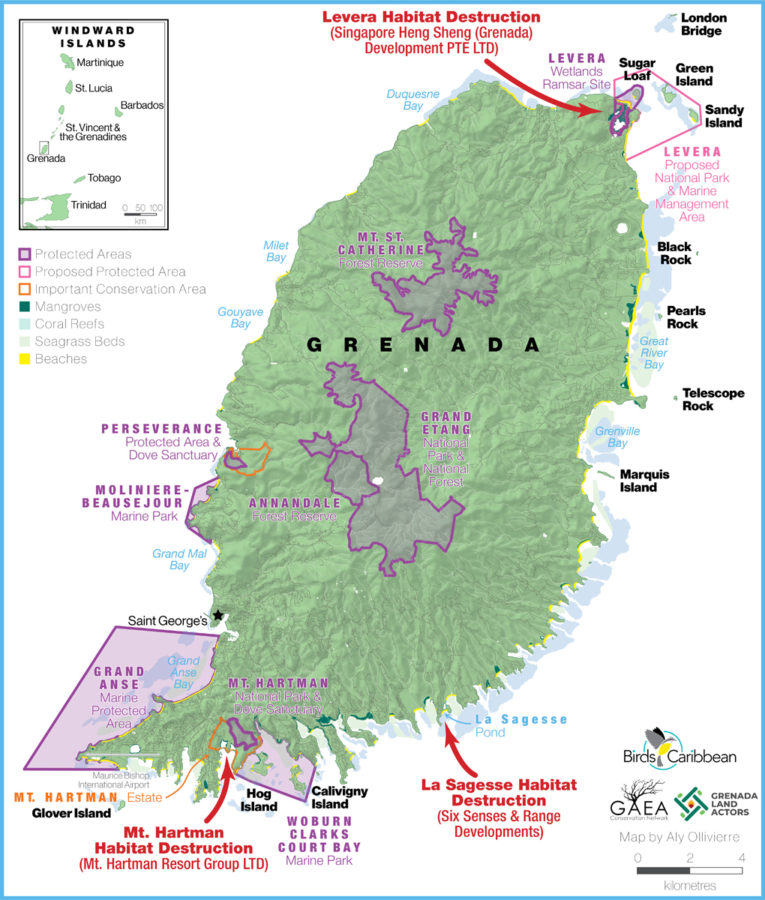












































































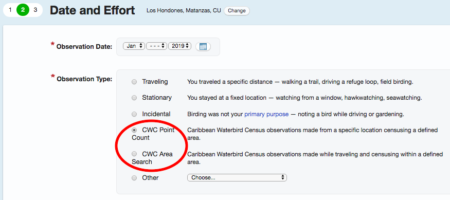
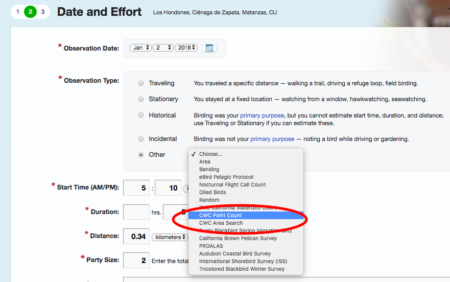




















































































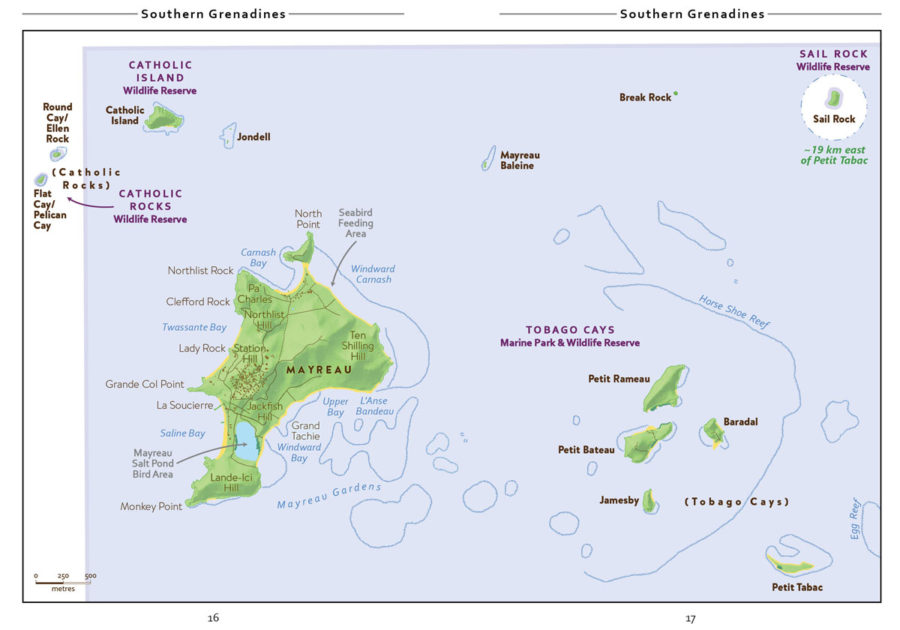
 Birds of the Transboundary Grenadines
Birds of the Transboundary Grenadines