Celebrate the Caribbean Endemic Bird Festival (CEBF) with us! Our theme in 2023 is “Water: Sustaining Bird Life” highlighting the importance of water conservation to both humans and birds. Have fun learning about a new endemic bird every day. We have colouring pages, puzzles, activities, and more. Download for free and enjoy nature with your family at home.
Endemic Bird of the Day: Bahama Mockingbird
In The Bahamas, when we hear the “trashers” singing, we know spring is upon us. Their rich soulful song is very pleasing to the ears of birders and nature lovers alike. But, there is more to love about these amazing birds than just their song! Here are some fascinating facts about the Bahama Mockingbird.
The Bahama Mockingbird is slightly larger than its Northern Mockingbird cousin and lacks the large white patches on the wings. It has grayish brown plumage with streaks on its sides and a thin white band on the base of its tail feathers. Females are slightly smaller and have a shorter tail. Juveniles have more densely spotted underparts. Their song is rich and melodious, though not as varied as the Northern Mockingbird. Bahamians locally refer to both species as “Trashers.”
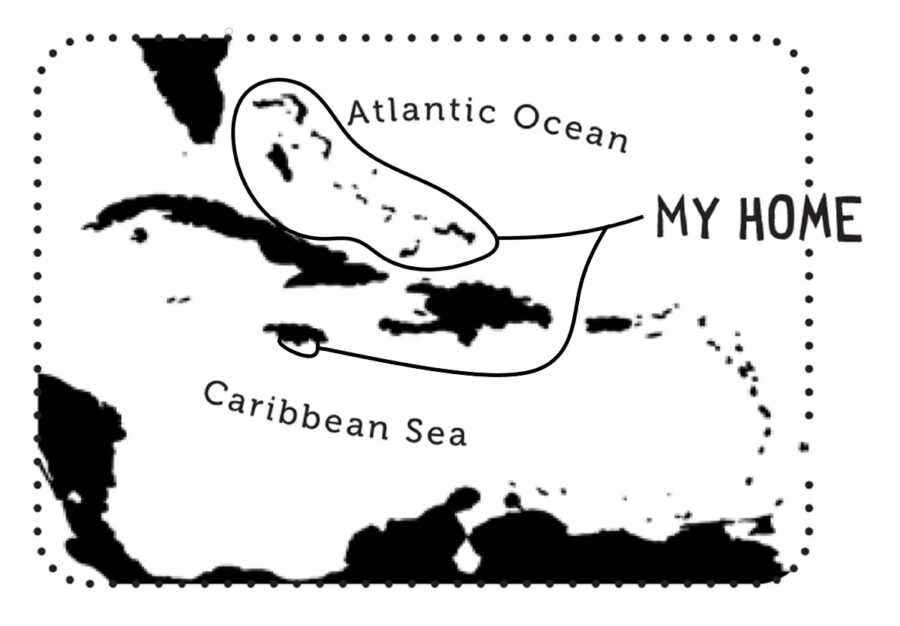
The Bahama Mockingbird, Mimus gundlachii, was named after the German Ornithologist Johannes Christoph Gundlach who spent most of his working life in Cuba (1810-1896). If you’re wondering why the Bahama Mockingbird was named after a German ornithologist living in Cuba, that’s because this bird is not just endemic to The Bahamas.
Their current distribution is mainly in the Lucayan Archipelago (The Bahamas and Turks and Caicos Islands), the Camagüey Archipelago of Cuba (Cayo Coco Cays) and a small area in Southern Jamaica. Historically, this species was also found in Puerto Rico. Genetically, the Bahama Mockingbird is more closely related to Galapagos Mockingbirds than the Northern Mockingbird. But, Bahama and Northern Mockingbirds do sometimes inter-breed!
In The Bahamas, the Bahama Mockingbird is found throughout the archipelago but appears to have its highest concentration in the central Bahamas, especially on Cat Island. Throughout its range, it prefers arid areas and is found in dry forests and scrub habitats. Unlike its northern cousin, it is mainly found in intact native habitats and tends to avoid urban areas.
Bahama Mockingbirds are omnivorous; this means they feed on arthropods, small vertebrates, and fruit. They forage mostly on the ground, sifting through leaf litter and turning small stones with their bills.
Like the Northern Mockingbird, the Bahama Mockingbird builds a cup-shaped nest out of twigs and plant fibers. Both male and female participate in nest building. Clutch size is between 2-3 creamy to pinkish-white eggs with reddish brown speckles. Both parents raise the chicks. Nests are usually located between 0.5m and 4.5m off the ground but they will sometimes even build their nest on the ground.
Whilst not a threatened species, the Bahama Mockingbird has a restricted range, making it highly susceptible to habitat loss caused by climate change and unsustainable development. In The Bahamas the population may be declining due to competition with the Northern Mockingbird for resources like food and nesting sites. Learn more about this species, including its range, photos, and calls here.
Thanks to Scott Johnson for the text!
Colour in the Bahama Mockingbird
Download our West Indies Endemic Bird colouring page. Use the photos below as your guide, or you can look up pictures of the bird online or in a bird field guide if you have one. Share your coloured-in page with us by posting it online and tagging us @BirdsCaribbean #CEBFfromthenest
Listen to the song of the Bahama Mockingbird
The song of the Bahama Mocking bird is a series of phrases, each repeated several times.
Puzzle of the Day
Click on the image below to do the puzzle. You can make the puzzle as easy or as hard as you like – for example, 6, 8, or 12 pieces for young children, all the way up to 1,024 pieces for those that are up for a challenge!




Activity of the Day
FOR KIDS AND ADULTS: With lots more Caribbean endemic birds to enjoy and colour in during the coming weeks take a look at our colouring-in guide. This will give you some hints and tips on how to make your endemic birds look even more beautiful! Share your coloured-in page with us by posting it online and tagging us @BirdsCaribbean #CEBFfromthenest
Enjoy this video of a Bahama Mockingbird foraging in the wild!
If you want to find out more about our conservation work and BirdsCaribbean’s bird banding program you an read all about our bird banding workshop – which was held in the Bahamas in 2022.



One comment
Comments are closed.