Celebrate World Migratory Bird Day (WMBD) with us in 2022! This year’s theme is “Dim The Lights for Birds at Night”. Have fun learning about a new migratory bird every day. We have colouring pages, puzzles, activities, and more. Download for free and enjoy nature with your family at home.
Migratory Bird of the Day: Ruddy Duck
A common member of the stifftail family, the Ruddy Duck is a small, compact duck with a scoop-shaped bill. This duck has a long, stiff, spiky-looking tail often held upright. The Male has a black cap and bright white cheeks. During the breeding season, he sports a bright sky-blue bill and chestnut-coloured upperparts. He pairs this ‘ensemble’ with unusual but entertaining courtship displays. In the non-breeding season males are a bit less flashy with -brown upperparts and blackish bills. Females and immatures are brown overall with a dark cap and a distinct dark stripe across the pale cheek.
When breeding males perform a ‘bubbling’ display, the male will hold his tail straight up while striking his bill against his inflated neck. Bubbles are created in the water as air is forced from the feathers. A courting male may also drop his tail and run across the water, making popping sounds with his feet. Males also utters a nasal “raa-anh” call during courtship displays, but outside the breeding season these small ducks are mainly silent .
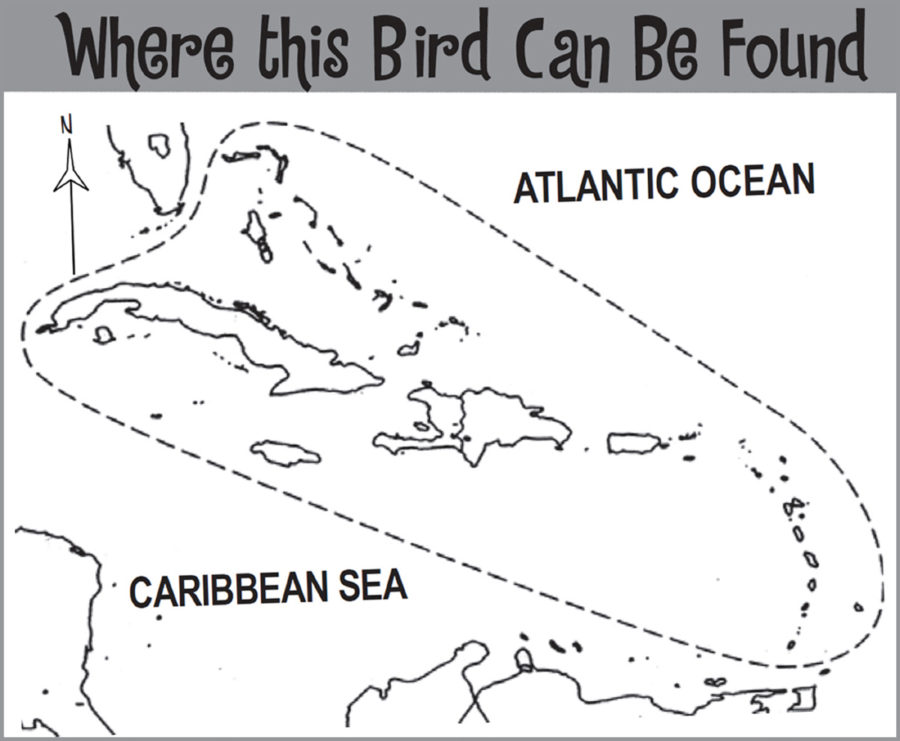
Ruddy Ducks are resident in parts in the Caribbean, found in the Bahamas, Greater Antilles, Virgin Islands and Barbados. Here they use open fresh-water and brackish ponds and lagoons. They feed mainly on aquatic insects, crustaceans, and other invertebrates, as well as small amounts of aquatic plants and seeds. They forage almost exclusively by diving, but are occasionally seen skimming food from the water surface. During fall and winter the Caribbean population is swelled by migratory Ruddy Ducks that breed in the Prairie Pothole region of North America. After breeding they head south to the Caribbean as well as the Gulf Coast, Mexico, and East Coast of the US to spend the winter.
Since Ruddy Ducks depend upon wetlands for their survival, they are directly impacted by threats to these areas such as pollution, habitat loss, and invasive species. It is vital to conserve and protect our wetlands. They provide habitats for the Ruddy Duck and many other species.They also provide invaluable services to humans such as flood protection, improved water quality, natural products, recreation, and so much more! Learn more about this species, including its range, photos, and calls here.
Colour in the Ruddy Duck
Download the Migratory Birds of the Day Colouring Page! Use the picture above and the photos on this page as your guide, or you can look up pictures of the bird online or in a bird field guide if you have one. Share your coloured-in page with us by posting it online and tagging us @BirdsCaribbean #WMBD2022Carib
Listen to the calls of the Ruddy Duck
Outside the breeding season Ruddy Ducks are often silent, but you might hear a nasal “raanh” call
Puzzles of the Day
Click on the images below to do the puzzle. You can make the puzzle as easy or as hard as you like – for example, 6, 8, or 12 pieces for young children, all the way up to 1,024 pieces for those that are up for a challenge!


Activity of the Day
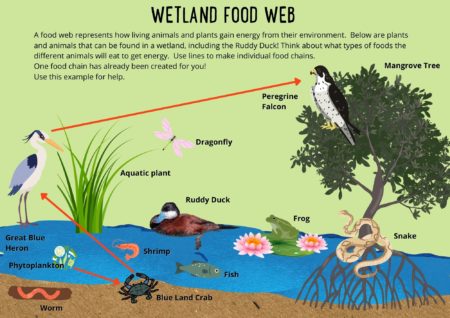 FOR KIDS: Ruddy Ducks can be found on ponds, reservoirs and in other wetlands all teaming with life! Ruddy Ducks like to feed on invertebrates and small crustaceans as well as plants. But within a wetland ecosystem all sorts of interactions take place as each animal living there looks for enough food to eat. A food web represents how living animals and plants gain energy from their environment. Take a look at our wetland ecosystem, including the Ruddy Duck, and see how many different links you can find! Think about what types of foods the different animals will eat to get energy. Use lines to make individual food chains. You can find some answers here.
FOR KIDS: Ruddy Ducks can be found on ponds, reservoirs and in other wetlands all teaming with life! Ruddy Ducks like to feed on invertebrates and small crustaceans as well as plants. But within a wetland ecosystem all sorts of interactions take place as each animal living there looks for enough food to eat. A food web represents how living animals and plants gain energy from their environment. Take a look at our wetland ecosystem, including the Ruddy Duck, and see how many different links you can find! Think about what types of foods the different animals will eat to get energy. Use lines to make individual food chains. You can find some answers here.
FOR KIDS AND ADULTS: Enjoy this video of a male Ruddy Duck feeding in the wild! He is diving down to find food, perhaps he is looking for some aquatic vegetation or invertebrates? Notice that now the breeding season is over this male has a black bill (rather than the blue one he has when breeding).