Want to go birding? Here are 10 tips to get you started!

 Stop, Look and Listen. Birds are everywhere – you don’t need to know anything about birds to get enjoyment from watching them – in your garden, at the beach, on your way to work – providing attraction and pleasure for us all. Your eyes and ears are all you need to start watching birds. Start looking at bird shapes, sizes, colors, posture, and where they live (habitat). Are they small like a bananaquit or large like a hawk? Is the tail long and pointed or short and forked? Are they all one color or multi-color? Are they feeding on the ground or high in trees? Do they hang in groups or solo? Take a cup of coffee out to your porch in the morning and listen to their calls and songs – you’ll soon start to notice differences between species. Do they sing with a pleasant song or with a constant trill? You’ll start to find patterns and learn to recognize your local neighborhood birds!
Stop, Look and Listen. Birds are everywhere – you don’t need to know anything about birds to get enjoyment from watching them – in your garden, at the beach, on your way to work – providing attraction and pleasure for us all. Your eyes and ears are all you need to start watching birds. Start looking at bird shapes, sizes, colors, posture, and where they live (habitat). Are they small like a bananaquit or large like a hawk? Is the tail long and pointed or short and forked? Are they all one color or multi-color? Are they feeding on the ground or high in trees? Do they hang in groups or solo? Take a cup of coffee out to your porch in the morning and listen to their calls and songs – you’ll soon start to notice differences between species. Do they sing with a pleasant song or with a constant trill? You’ll start to find patterns and learn to recognize your local neighborhood birds!
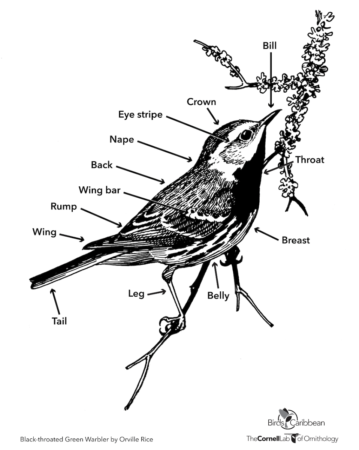
 Zoom In. If you decide to get more serious about birding, find a pair of binoculars to take a closer look – any old binoculars will do to start. If you’re looking to buy binoculars, we recommend 7 x 35 or 8 x 42. Vortex, Nikon, Bushnell, and Celestron all have some great options for beginner birders. No binoculars? Try a camera to take photos – even a phone camera can take a good bird photo. Use your binoculars or camera to really look at the detail of the bird. Is the bill small and fine like a warbler’s or short and stout like a seed-cracking grassquit? Does the bird have distinctive patches or patterns of color that stand out, called field marks, or is it more plain? Are the legs black, yellow, green or pink? Does it fly with regular wingbeats, hover, or soar?
Zoom In. If you decide to get more serious about birding, find a pair of binoculars to take a closer look – any old binoculars will do to start. If you’re looking to buy binoculars, we recommend 7 x 35 or 8 x 42. Vortex, Nikon, Bushnell, and Celestron all have some great options for beginner birders. No binoculars? Try a camera to take photos – even a phone camera can take a good bird photo. Use your binoculars or camera to really look at the detail of the bird. Is the bill small and fine like a warbler’s or short and stout like a seed-cracking grassquit? Does the bird have distinctive patches or patterns of color that stand out, called field marks, or is it more plain? Are the legs black, yellow, green or pink? Does it fly with regular wingbeats, hover, or soar?

 Read Up. Try and get hold of a bird field guide for your region or island – Birds of the West Indies is an excellent one for the Caribbean. Spend some time getting familiar with the layout of the book. Many books will have checklists and distribution maps of birds you might expect to find in your area. Look at the pictures, and read the species description as it’ll tell you what distinguishing features to look for. You’ll also find it useful to read the habitat description to compare with where you saw the bird. Check out the vocalization descriptions too – you can also find many audio recordings of bird calls online. If you want a mobile version, download the Merlin app and the bird pack for your region. Merlin comes equipped with range maps, photos, description, and audio calls all in the convenience of your phone!
Read Up. Try and get hold of a bird field guide for your region or island – Birds of the West Indies is an excellent one for the Caribbean. Spend some time getting familiar with the layout of the book. Many books will have checklists and distribution maps of birds you might expect to find in your area. Look at the pictures, and read the species description as it’ll tell you what distinguishing features to look for. You’ll also find it useful to read the habitat description to compare with where you saw the bird. Check out the vocalization descriptions too – you can also find many audio recordings of bird calls online. If you want a mobile version, download the Merlin app and the bird pack for your region. Merlin comes equipped with range maps, photos, description, and audio calls all in the convenience of your phone!
 Find your Flock! If you’re getting hooked, it’s now time to find a local birding group. Meeting more experienced birders will help you learn to identify species that might be difficult to distinguish. All bird species are different from each other in some way, but some are so similar they can take years to become expert at identifying. You might even sign up for the “rare bird alerts” on eBird so you can know when unusual species have been found in your area!
Find your Flock! If you’re getting hooked, it’s now time to find a local birding group. Meeting more experienced birders will help you learn to identify species that might be difficult to distinguish. All bird species are different from each other in some way, but some are so similar they can take years to become expert at identifying. You might even sign up for the “rare bird alerts” on eBird so you can know when unusual species have been found in your area!

 Make your Yard Bird-friendly. Provide some bushes and trees for cover and plant native plants that have flowers, fruit, and/or seeds that birds can eat. A free ebook, Heritage Plants, features dozens of native Caribbean plants that are of particular value to local birds as well as techniques for creating a great backyard bird habitat. A free webinar, Native Plants for a Bird-Friendly Backyard, features Caribbean bird, plant and habitat restoration experts.
Make your Yard Bird-friendly. Provide some bushes and trees for cover and plant native plants that have flowers, fruit, and/or seeds that birds can eat. A free ebook, Heritage Plants, features dozens of native Caribbean plants that are of particular value to local birds as well as techniques for creating a great backyard bird habitat. A free webinar, Native Plants for a Bird-Friendly Backyard, features Caribbean bird, plant and habitat restoration experts.
 Bring the Birds to You! It’s easy to make your yard a bird haven. Purchase an inexpensive bird feeder, or better yet make one from materials you have laying around your house! Here’s a helpful video to get you started. Nectar feeders are also a great way to attract hummingbirds, Bananaquits, and even warblers. Providing water can be as simple as putting out a clay pot dish or plastic roller paint pan. Fill it with fresh water every day and you will soon have avian visitors coming for a drink or a bath.
Bring the Birds to You! It’s easy to make your yard a bird haven. Purchase an inexpensive bird feeder, or better yet make one from materials you have laying around your house! Here’s a helpful video to get you started. Nectar feeders are also a great way to attract hummingbirds, Bananaquits, and even warblers. Providing water can be as simple as putting out a clay pot dish or plastic roller paint pan. Fill it with fresh water every day and you will soon have avian visitors coming for a drink or a bath.

 Talk the Talk. Learn the lingo of experienced birders, like Lifer (a bird species that you’ve seen for the first time); Twitcher (a birder obsessed with keeping a life list and going to great efforts to add to it), Dipping (missing out on the bird you specifically went looking for); Pishing (making a sound, pishhhh pishhhh, with your lips to get songbirds to come out or come closer); Peeps (a term used to refer to small, almost identical-looking sandpipers); LBJs (little brown jobs – a blanket term for drab songbirds that are difficult to distinguish); Patch (a local area frequented by birders); Spark Bird (the species of bird that sparked a life-long passion for birding); Vagrant (a bird straying well outside of its usual range); or Skulker (a cryptic, notoriously difficult bird to see).
Talk the Talk. Learn the lingo of experienced birders, like Lifer (a bird species that you’ve seen for the first time); Twitcher (a birder obsessed with keeping a life list and going to great efforts to add to it), Dipping (missing out on the bird you specifically went looking for); Pishing (making a sound, pishhhh pishhhh, with your lips to get songbirds to come out or come closer); Peeps (a term used to refer to small, almost identical-looking sandpipers); LBJs (little brown jobs – a blanket term for drab songbirds that are difficult to distinguish); Patch (a local area frequented by birders); Spark Bird (the species of bird that sparked a life-long passion for birding); Vagrant (a bird straying well outside of its usual range); or Skulker (a cryptic, notoriously difficult bird to see).
 Take Notes. Get a small notebook to record your observations. Taking notes on date, location, weather conditions, and detailed information on the birds seen will improve your powers of observation and memory and help you remember each birding session or trip accurately. You should describe in detail the field marks of any unidentified birds and later look through your field guides. With good notes, there is a strong chance you will be able to identify the bird later. Keep track of what you are seeing, i.e., your checklists, and at the same time contribute to science with a powerful app called eBird. (If you’re in the Caribbean, use eBird Caribbean). eBird is an invaluable tool for birders, storing all your sightings, so you know when a bird is a new lifer. You can also explore species range maps and learn about the best birding spots, called hotspots, near you. That’s it! You’re on your way to becoming a birder and a citizen scientist!
Take Notes. Get a small notebook to record your observations. Taking notes on date, location, weather conditions, and detailed information on the birds seen will improve your powers of observation and memory and help you remember each birding session or trip accurately. You should describe in detail the field marks of any unidentified birds and later look through your field guides. With good notes, there is a strong chance you will be able to identify the bird later. Keep track of what you are seeing, i.e., your checklists, and at the same time contribute to science with a powerful app called eBird. (If you’re in the Caribbean, use eBird Caribbean). eBird is an invaluable tool for birders, storing all your sightings, so you know when a bird is a new lifer. You can also explore species range maps and learn about the best birding spots, called hotspots, near you. That’s it! You’re on your way to becoming a birder and a citizen scientist!

 Respect. Birding should be a fun experience for everyone. Make sure that you’re respecting the space of the birds. While it can be tempting to get that NatGeo shot, make sure you’re not upsetting a nesting bird that is already expending a lot of energy breeding and maintaining a territory. And respect extends out to your fellow birders. Your neighbor might have the perfect vagrant patch, but make sure you always ask permission before birding someone’s property. This extends to National Parks too, those visitor fees help keep the park a safe space for birds and birders alike! Don’t skimp out on park fees and make sure you take all your trash back out with you.
Respect. Birding should be a fun experience for everyone. Make sure that you’re respecting the space of the birds. While it can be tempting to get that NatGeo shot, make sure you’re not upsetting a nesting bird that is already expending a lot of energy breeding and maintaining a territory. And respect extends out to your fellow birders. Your neighbor might have the perfect vagrant patch, but make sure you always ask permission before birding someone’s property. This extends to National Parks too, those visitor fees help keep the park a safe space for birds and birders alike! Don’t skimp out on park fees and make sure you take all your trash back out with you.
 Practice, Practice, Practice . . . and Have Fun! Like anything else in life, to become a really good birder takes practice, in other words, lots of time in the field observing, listening, and studying your field guide. Before you know it, you’ll be identifying those LBJs and Peeps! Whatever level you’re at, the most important thing is to get out there and enjoy seeing some birds!
Practice, Practice, Practice . . . and Have Fun! Like anything else in life, to become a really good birder takes practice, in other words, lots of time in the field observing, listening, and studying your field guide. Before you know it, you’ll be identifying those LBJs and Peeps! Whatever level you’re at, the most important thing is to get out there and enjoy seeing some birds!

Resources
Some of BirdsCaribbean’s flagship programs can help you or your kids to get involved in bird watching. Check out our BirdSleuth and Caribbean Waterbird Census programs to find out more. Wondering where to go? Check out the Caribbean Birding Trail.
Support Bird Conservation
If you’d like to get more involved in the protection and preservation of Caribbean birds, consider joining the BirdsCaribbean community! You can support our work in a number of ways: volunteering, bird monitoring, and becoming a member. Membership has many benefits, including discounts on annual conferences and events; and a free annual subscription to Birds of the World, the most comprehensive database of ALL the world’s bird species (a $49 value).
Sign up for our monthly newsletter, to stay informed on BirdsCaribbean news and activities near you, and follow us on social media @BirdsCaribbean!

Useful Links
Check out these Bird ID webinars and short videos on BirdsCaribbean’s YouTube channel:
- Waterbird Identification Part I: Herons, Egrets, Ducks, Marsh Birds, Seabirds
- Waterbird Identification Part II: Shorebirds
- Conociendo las aves endémicas (Getting to know the endemic birds) CEBF Webinar
- Bird ID and Natural History Shorts
Additional links to help you get better at birding:
- Birding Basics at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Watching Birds at the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds
…