Celebrate the Caribbean Endemic Bird Festival (CEBF) with us in our virtual “From the Nest” edition! Have fun learning about a new endemic bird every day. We have colouring pages, puzzles, activities, and more. Download for free and enjoy nature with your family at home.
Endemic Bird of the Day: Puerto Rican Emerald
 The Puerto Rican Emerald (Chlorostilbon maugeaus), or Zumbadorcito de Puerto Rico in Spanish, is an endemic hummingbird found only in the archipelago of Puerto Rico. Measuring from 3.5 to 4 inches and weighing approximately 3 g, it is the smallest bird species in the island. It is not much larger than the smallest hummingbird species of the world, the Bee Hummingbird from Cuba, which weighs only 1.8 g. For comparison, a penny weighs 2.5 g, similar to these tiny birds!
The Puerto Rican Emerald (Chlorostilbon maugeaus), or Zumbadorcito de Puerto Rico in Spanish, is an endemic hummingbird found only in the archipelago of Puerto Rico. Measuring from 3.5 to 4 inches and weighing approximately 3 g, it is the smallest bird species in the island. It is not much larger than the smallest hummingbird species of the world, the Bee Hummingbird from Cuba, which weighs only 1.8 g. For comparison, a penny weighs 2.5 g, similar to these tiny birds!
The Puerto Rican Emerald is sexually dimorphic, meaning that males and females look different. The male has iridescent green feathers on its body and a black tail, while the female has white underparts and white outer tail feathers. This hummingbird can be distinguished from other hummingbirds in the archipelago by its shorter, straighter bill, and black forked tail. Emeralds are distributed throughout forests and woodlands from the coast up to the mountains. They are highly territorial, often defending territories with intense aerial pursuits.
The Puerto Rican Emerald mainly feeds on nectar taken from a variety of brightly colored, scented small flowers of trees, herbs, shrubs and epiphytes. They use their long, extendible, straw-like tongues to retrieve the nectar while hovering with their tails cocked. Sometimes they may be seen hanging on the flower while feeding. Many native and cultivated plants on whose flowers these birds feed heavily rely on them for pollination. With its smaller size, this species feeds on the nectar of flowers with shorter corollas (petals). Sometimes they reach the nectaries from larger flowers by piercing the base of the flower. This is a form of “nectar robbery” because it does not provide the essential service of pollination to the plant. Emeralds also take some small spiders and insects, especially females, which provide an important source of protein during the breeding season.
Puerto Rican Emeralds may visit local hummingbird feeders for some sugar water, or drink out of bird baths or water fountains where they will either hover and sip water, or they will perch on the edge and drink. Do you have Puerto Rican Emeralds visiting your yard? If not, entice these colorful gems by providing native flowering plants that they are fond of, like Malvaviscus penduliflorus (Turks cap, sleeping hibiscus, carriaquillo), Hamelia patens (firecracker bush, firebush), and Odontonema sp (cardinal’s guard). You can also enjoy their presence by providing a feeder. Just be sure to clean it and refill it every couple of days! Learn more about this species, including its range, photos, and calls here.
Colour in the Puerto Rican Emerald!
Download the page from Endemic Birds of the West Indies Colouring Book. Use the drawing above or photo below as your guide, or you can look up pictures of the bird online or in a bird field guide if you have one. Share your coloured-in page with us by posting it online and tagging us @BirdsCaribbean #CEBFfromthenest
Listen to the song of the Puerto Rican Emerald
The Puerto Rican Emerald‘s song is a repeated twittering phrase of high-pitched descending notes, tseereetseetseetsee-tslew-tslew-tslew-tslew-tslew. Calls include a constantly repeated high-pitched tsik and irregular series si..si..sik-sik…tsik. (other birds heard in this recording: Black-faced Grassquit, Puerto Rican Tody, Puerto Rican Vireo, Elfin Woods Warbler, Puerto Rican Woodpecker).
Puzzle of the Day
Click on the image below to do the puzzle. You can make the puzzle as easy or as hard as you like – for example, 6, 8, or 12 pieces for young children, all the way up to 1,024 pieces for those that are up for a challenge!
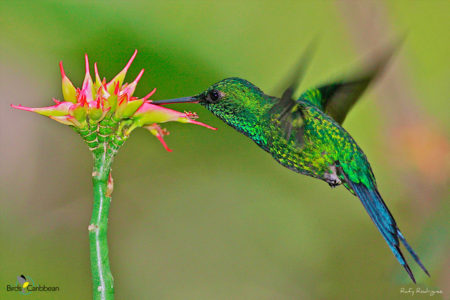

Activity of the Day
FOR KIDS & ADULTS: Enjoy the videos below by Aves Puerto Rico Felpe. First, a male sipping nectar from flowers, including slow motion of the bird hovering while it feeds. The second incredible video shows a female feeding her chick, newly fledged and out of the nest, but still being fed by Mom. The third video shows 2 chicks (male and female) in the nest at 17 days old. Their feathers are growing and they will fledge soon – they are nearly too big for the tiny cup-like nest!
The female alone builds the nest using plant fiber, wild cotton, moss, cobweb and its saliva; and decorates it with lichens. She lays 2 eggs and incubates them for about 14-16 days. Chicks fledge (leave the nest) at about 20-22 days old.
Here’s a recipe for making nectar (sugar water) for your hummingbird feeder.
And here is a free e-book about native plants for a bird-friendly yard, including suggestions for flowering plants that are popular with hummingbirds.

